
by admin | Nov 14, 2017 | ACA, Group Benefit Plans, Human Resources, IRS
 October was a busy month in the employee benefits world. President Trump announced a new Acting Secretary for the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Eric Hargan fills the position vacated by Tom Price, who resigned in late September 2017. The U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) issued a proposed rule to delay a disability claims procedure regulation’s applicability date and HHS released its proposed rule on benefits and payment parameters for 2019. The U.S. Department of the Treasury (Treasury) issued its Priority Guidance Plan for projects it intends to complete during the first half of 2018.
October was a busy month in the employee benefits world. President Trump announced a new Acting Secretary for the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Eric Hargan fills the position vacated by Tom Price, who resigned in late September 2017. The U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) issued a proposed rule to delay a disability claims procedure regulation’s applicability date and HHS released its proposed rule on benefits and payment parameters for 2019. The U.S. Department of the Treasury (Treasury) issued its Priority Guidance Plan for projects it intends to complete during the first half of 2018.
DOL Proposes Delay to Final Disability Claims Procedures Regulations’ Applicability Date
The DOL issued a proposed rule to delay the applicability date of its final rule that amends the claims procedure requirements applicable to ERISA-covered employee benefit plans that provide disability benefits. The DOL’s Fact Sheet contains a summary of the final rule’s requirements.
The DOL is delaying the applicability date from January 1, 2018, to April 1, 2018, to consider whether to rescind, modify, or retain the regulations and to give the public an additional opportunity to submit comments and data concerning the final rule’s potential impact.
CMS Releases 2019 Benefits Payment and Parameters Proposed Rule
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) released a proposed rule and fact sheet for the 2019 Benefit Payment and Parameters. The proposed rule is intended to increase individual market flexibility, improve program integrity, and reduce regulatory burdens associated with the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) in many ways, including updates and annual provisions to:
- Essential health benefits
- Small Business Health Options Program (SHOP)
- Special enrollment periods (SEPs)
- Exemptions
- Termination effective dates
- Medical loss ratio (MLR)
CMS usually finalizes the Benefit Payment and Parameters rule in the first quarter of the year following the proposed rule’s release. November 27, 2017, is the due date for public comments on the proposed rule.
Almost all the topics addressed in the proposed rule would affect the individual market and the Exchanges, particularly the Small Business Health Options Program (SHOP) Exchanges.
Of interest to small group health plans, CMS proposes to change how states will select essential health benefits benchmark plans. If CMS keeps this change in its final rule, then it will affect non-grandfathered small group health plans for benefit years 2019 and beyond.
Treasury Issues its Priority Guidance Plan
The Treasury issued its 2017-2018 Priority Guidance Plan that lists projects that it intends to complete by June 30, 2018, including:
- Guidance on issues related to the employer shared responsibility provisions
- Regulations regarding the excise tax on high cost employer-provided coverage (“Cadillac tax”)
- Guidance on Qualified Small Employer Health Reimbursement Arrangements (QSE HRAs)
By Danielle Capilla
Originally Published By United Benefit Advisors

by admin | Nov 9, 2017 | ACA, Human Resources, IRS

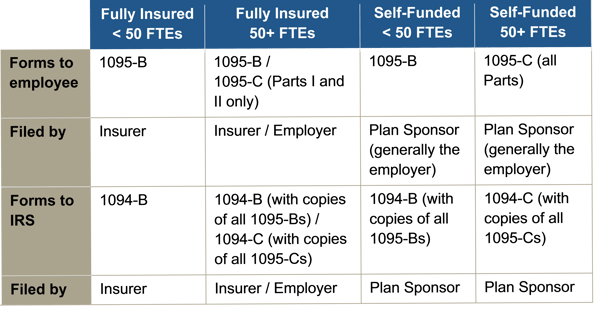
Instructions for both the 1094-B and 1095-B and the 1094-C and 1095-C were released, as were the forms for 1094-B, 1095-B, 1094-C, and 1095-C.
Reporting will be due early in 2018, based on coverage in 2017. For calendar year 2017, Forms 1094-C, 1095-C, 1094-B, and 1095-B must be filed by February 28, 2018, or April 2, 2018, if filing electronically. Statements to employees must be furnished by January 31, 2018. In late 2016, a filing deadline was provided for forms due in early 2017, however it is unknown if that extension will be provided for forms due in early 2018. Until employers are told otherwise, they should plan on meeting the current deadlines.
All reporting will be for the 2017 calendar year, even for non-calendar year plans.
The reporting requirements are in Sections 6055 and 6056 of the ACA. The major reporting requirements are:

by admin | Nov 7, 2017 | Benefit Management, Health Plan Benchmarking
 The findings of our 2017 Health Plan Survey show a continuation of steady trends and some surprises. It’s no surprise, however, that costs continue to rise. The average annual health plan cost per employee for all plan types is $9,934, an increase from 2016, when the average cost was $9,727. There are significant cost differences when you look at the data by plan type.
The findings of our 2017 Health Plan Survey show a continuation of steady trends and some surprises. It’s no surprise, however, that costs continue to rise. The average annual health plan cost per employee for all plan types is $9,934, an increase from 2016, when the average cost was $9,727. There are significant cost differences when you look at the data by plan type.
Cost Detail by Plan Type
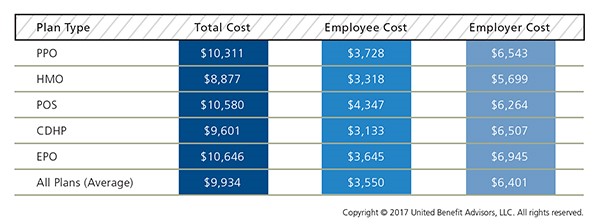
PPOs continue to cost more than the average plan, but despite this, PPOs still dominate the market in terms of plan distribution and employee enrollment. PPOs have seen an increase in total premiums for single coverage of 4.5% and for family coverage of 2.2% in 2017 alone.
HMOs have the lowest total annual cost at $8,877, as compared to the total cost of a PPO of $10,311. Conversely, CDHP plan costs have risen 2.2% from last year. However, CDHP prevalence and enrollment continues to grow in most regions, indicating interest among both employers and employees.
Across all plan types, employees’ share of total costs rose 5% while employers’ share stayed nearly the same. Employers are also further mitigating their costs by reducing prescription drug coverage, and raising out-of-network deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums.
More than half (54.8%) of all employers offer one health plan to employees, while 28.2% offer two plan options, and 17.1% offer three or more options. The percentage of employers now offering three or more plans decreased slightly in 2017, but still maintains an overall increase in the last five years as employers are working to offer expanded choices to employees either through private exchange solutions or by simply adding high, medium-, and low-cost options; a trend UBA Partners believe will continue. Not only do employees get more options, but employers also can introduce lower-cost plans that may attract enrollment, lower their costs, and meet ACA affordability requirements.
By Bill Olson
Originally Published By United Benefit Advisors

by admin | Nov 3, 2017 | Group Benefit Plans, HIPAA, Human Resources
 Employers who are designing a health and welfare benefit plan for their employees often wonder about the rules relating to setting premiums for employees. Employers generally have significant flexibility in this part of their plan’s design. Common structures contemplated by employers include, but are not limited to:
Employers who are designing a health and welfare benefit plan for their employees often wonder about the rules relating to setting premiums for employees. Employers generally have significant flexibility in this part of their plan’s design. Common structures contemplated by employers include, but are not limited to:
- Charging all employees a flat amount for their health plan
- Charging employees a percentage of the premium for the health plan, with the percentage changing as employees move between tiers (self, self plus one, self plus family)
- Giving employees a set dollar amount that they can use to offset the cost of whatever plan and plan tier they enroll in
Employers are also interested in setting different contribution structures for different groups of employees. Sometimes this is due to a geographic difference between employees, job types, staff versus management, and more. Employers may wish to give lower-paid employees more employer-provided money; sometimes employers wish to give managers or executive staff more employer-provided money.
Employers should be aware that there are different nondiscrimination requirements to consider.
Generally, under HIPAA non-discrimination rules, employers have discretion when structuring their benefits plans and may make distinctions among employee populations regarding access to and the level of benefits offered. Plans may differ among employees only on “bona fide employment-based classifications” consistent with the employer’s usual business practice. Examples that would satisfy this requirement include salaried, hourly, full-time, part-time, type of job, geographic location, date of hire, division, subsidiary, business unit, and profit center distinctions.
If an employer’s proposed structure meets these basic HIPAA requirements, then the employer needs to review the applicable nondiscrimination requirements under Internal Revenue Code Section 125 (for cafeteria plans) and Section 105(h) (for self-funded plans). If the employer’s plan is subject to these rules, at a most basic level, the plan cannot favor highly compensated individuals. Sometimes an innocent plan design can lead to an employer failing the nondiscrimination requirements under Section 125 or 105(h) without the employer intentionally favoring the highly compensated employees. Many employers also erroneously assume that none of their employees fall into the “highly compensated” category, so the rules do not apply to them. As a best practice, any time an employer has a plan design with different levels of employer contributions, the employer should run the applicable testing to ensure its plan is compliant.
Under Section 125, benefit plans cannot discriminate in favor of highly compensated individuals or key employees.
By Danielle Capilla
Originally Published By United Benefit Advisors

by admin | Nov 1, 2017 | ACA, Compliance
 Two tri-agency (Internal Revenue Service, Employee Benefits Security Administration, and Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services) Interim Final Rules were released and became effective on October 6, 2017, and will be published on October 31, 2017, allowing a greater number of employers to opt out of providing contraception to employees at no cost through their employer-sponsored health plan. The expanded exemption encompasses all non-governmental plan sponsors that object based on sincerely held religious beliefs, and institutions of higher education in their arrangement of student health plans. The exemption also now encompasses employers who object to providing contraception coverage on the basis of sincerely held moral objections and institutions of higher education in their arrangement of student health plans. Furthermore, if an issuer of health coverage (an insurance company) had sincere religious beliefs or moral objections, it would be exempt from having to sell coverage that provides contraception. The exemptions apply to both non-profit and for-profit entities.
Two tri-agency (Internal Revenue Service, Employee Benefits Security Administration, and Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services) Interim Final Rules were released and became effective on October 6, 2017, and will be published on October 31, 2017, allowing a greater number of employers to opt out of providing contraception to employees at no cost through their employer-sponsored health plan. The expanded exemption encompasses all non-governmental plan sponsors that object based on sincerely held religious beliefs, and institutions of higher education in their arrangement of student health plans. The exemption also now encompasses employers who object to providing contraception coverage on the basis of sincerely held moral objections and institutions of higher education in their arrangement of student health plans. Furthermore, if an issuer of health coverage (an insurance company) had sincere religious beliefs or moral objections, it would be exempt from having to sell coverage that provides contraception. The exemptions apply to both non-profit and for-profit entities.
The currently-in-place accommodation is also maintained as an optional process for exempt employers, and will provide contraceptive availability for persons covered by the plans of entities that use it (a legitimate program purpose). These rules leave in place the government’s discretion to continue to require contraceptive and sterilization coverage where no such objection exists. These interim final rules also maintain the existence of an accommodation process, but consistent with expansion of the exemption, the process is optional for eligible organizations. Effectively this removes a prior requirement that an employer be a “closely held for-profit” employer to utilize the exemption.
Employers that object to providing contraception on the basis of sincerely held religious beliefs or moral objections, who were previously required to offer contraceptive coverage at no cost, and that wish to remove the benefit from their medical plan are still subject (as applicable) to ERISA, its plan document and SPD requirements, notice requirements, and disclosure requirements relating to a reduction in covered services or benefits. These employers would be obligated to update their plan documents, SBCs, and other reference materials accordingly, and provide notice as required.
Employers are also now permitted to offer group or individual health coverage, separate from the current group health plans, that omits contraception coverage for employees who object to coverage or payment for contraceptive services, if that employee has sincerely held religious beliefs relating to contraception. All other requirements regarding coverage offered to employees would remain in place. Practically speaking, employers should be cautious in issuing individual policies until further guidance is issued, due to other regulations and prohibitions that exist.
By Danielle Capilla
Originally Published By United Benefit Advisors

 October was a busy month in the employee benefits world. President Trump announced a new Acting Secretary for the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Eric Hargan fills the position vacated by Tom Price, who resigned in late September 2017. The U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) issued a proposed rule to delay a disability claims procedure regulation’s applicability date and HHS released its proposed rule on benefits and payment parameters for 2019. The U.S. Department of the Treasury (Treasury) issued its Priority Guidance Plan for projects it intends to complete during the first half of 2018.
October was a busy month in the employee benefits world. President Trump announced a new Acting Secretary for the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Eric Hargan fills the position vacated by Tom Price, who resigned in late September 2017. The U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) issued a proposed rule to delay a disability claims procedure regulation’s applicability date and HHS released its proposed rule on benefits and payment parameters for 2019. The U.S. Department of the Treasury (Treasury) issued its Priority Guidance Plan for projects it intends to complete during the first half of 2018.





