
by admin | Oct 11, 2017 | ACA, ERISA, Group Benefit Plans

Two tri-agency (Internal Revenue Service, Employee Benefits Security Administration, and Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services) Interim Final Rules were released and became effective on October 6, 2017, and will be published on October 31, 2017, allowing a greater number of employers to opt out of providing contraception to employees at no cost through their employer-sponsored health plan. The expanded exemption encompasses all non-governmental plan sponsors that object based on sincerely held religious beliefs, and institutions of higher education in their arrangement of student health plans. The exemption also now encompasses employers who object to providing contraception coverage on the basis of sincerely held moral objections and institutions of higher education in their arrangement of student health plans. Furthermore, if an issuer of health coverage (an insurance company) had sincere religious beliefs or moral objections, it would be exempt from having to sell coverage that provides contraception. The exemptions apply to both non-profit and for-profit entities.
The currently-in-place accommodation is also maintained as an optional process for exempt employers, and will provide contraceptive availability for persons covered by the plans of entities that use it (a legitimate program purpose). These rules leave in place the government’s discretion to continue to require contraceptive and sterilization coverage where no such objection exists. These interim final rules also maintain the existence of an accommodation process, but consistent with expansion of the exemption, the process is optional for eligible organizations. Effectively this removes a prior requirement that an employer be a “closely held for-profit” employer to utilize the exemption.
Employers that object to providing contraception on the basis of sincerely held religious beliefs or moral objections, who were previously required to offer contraceptive coverage at no cost, and that wish to remove the benefit from their medical plan are still subject (as applicable) to ERISA, its plan document and SPD requirements, notice requirements, and disclosure requirements relating to a reduction in covered services or benefits. These employers would be obligated to update their plan documents, SBCs, and other reference materials accordingly, and provide notice as required.
Employers are also now permitted to offer group or individual health coverage, separate from the current group health plans, that omits contraception coverage for employees who object to coverage or payment for contraceptive services, if that employee has sincerely held religious beliefs relating to contraception. All other requirements regarding coverage offered to employees would remain in place. Practically speaking, employers should be cautious in issuing individual policies until further guidance is issued, due to other regulations and prohibitions that exist.
Background
As background, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) requires that non-grandfathered group health plans and health insurance issuers offering non-grandfathered group or individual health insurance coverage provide coverage of certain specified preventive services without cost sharing.
In 2011, the Departments issued regulations requiring coverage of women’s preventive services provided for in the Health Resources & Services Administration (HRSA) guidelines. The HRSA guidelines include all FDA-approved contraceptives, sterilization procedures, and patient education and counseling for women with reproductive capacity, as prescribed by the health care provider (collectively, contraceptive services).
Under the 2011 regulations, group health plans of “religious employers” (specifically defined in the law) are exempt from the requirement to provide contraceptive coverage.
In 2013, the Departments published regulations that provide an accommodation for eligible organizations that object on religious grounds to providing coverage for contraceptive services, but are not eligible for the exemption for religious employers. Under the accommodation, an eligible organization is not required to contract, arrange, pay for, or provide a referral for contraceptive coverage. The accommodation generally ensures that women enrolled in the health plan established by the eligible organization, like women enrolled in health plans maintained by other employers, receive contraceptive coverage seamlessly–that is, through the same issuers or third party administrators that provide or administer the health coverage furnished by the eligible organization, and without financial, logistical, or administrative obstacles.
In 2014, the U.S. Supreme Court decided Burwell v. Hobby Lobby. The Court held that the contraceptive coverage requirement substantially burdened the religious exercise of closely held for-profit corporations that had religious objections to providing contraceptive coverage and that the accommodation was a less restrictive means of provision coverage to their employees.
Because of Burwell v. Hobby Lobby, the Departments extended the accommodation to closely held for-profit entities. Under the accommodation, an eligible organization that objects to providing contraceptive coverage for religious reasons may either:
- Self-certify its objection to its health insurance issuer (to the extent it has an insured plan) or third party administrator (to the extent it has a self-funded plan) using a form provided by the Department of Labor (EBSA Form 700); or
- Self-certify its objection and provide certain information to the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) without using any particular form.
In 2016, in Zubik v. Burwell, the U.S. Supreme Court considered claims by several employers that, even with the accommodation provided in the regulations, the contraceptive coverage requirement violates the Religious Freedom Restoration Act of 1993 (RFRA). The Court heard oral arguments and ultimately remanded the case (and parallel RFRA cases) to the lower courts to give the parties “an opportunity to arrive at an approach going forward that accommodates [the objecting employers’] religious exercise while at the same time ensuring that women covered by [the employers’] health plans ‘receive full and equal health coverage, including contraceptive coverage.'”
Previously, Who Could Object and How
As provided in the 2015 final regulations, only certain organizations could object to providing contraception coverage. The final regulations provide two accommodations for eligible organizations to provide notice of a religious objection to the coverage of contraceptive services. Employers that object to providing contraceptive services will need to determine if they meet the criteria of an eligible organization in order to use one of the two accommodations. An eligible organization is an organization that meets all of the following requirements.
- Opposes providing coverage for some or all of any contraceptive items or services required to be covered on account of religious objections.
- Either is organized and operates as a nonprofit entity and holds itself out as a religious organization, or is organized and operates as a closely held for-profit entity, and the organization’s highest governing body (such as its board of directors, board of trustees, or owners, if managed directly by its owners) has adopted a resolution or similar action, under the organization’s applicable rules of governance and consistent with state law, establishing that it objects to covering some or all of the contraceptive services on account of the owner’s sincerely held religious beliefs.
- If both of the first two requirements are met, the organization must self-certify. The organization must make such self-certification or notice available for examination upon request by the first day of the first plan year to which the accommodation applies. The self-certification or notice must be executed by a person authorized to make the certification or notice on behalf of the organization, and must be maintained in a manner consistent with the record retention requirements under Section 107 of ERISA.
A “closely held for-profit entity” is defined in the regulations as an organization that:
- Is not a nonprofit entity;
- Has no publicly traded ownership interests (for this purpose, a publicly traded ownership interest is any class of common equity securities required to be registered under section 12 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934); and
- Has more than 50 percent of the value of its ownership interest owned directly or indirectly by five or fewer individuals, or has an ownership structure that is substantially similar thereto, as of the date of the entity’s self-certification or notice described in the requirements of an “eligible organization.”
To determine its ownership interest, the following rules apply:
- Ownership interests owned by a corporation, partnership, estate, or trust are considered owned proportionately by such entity’s shareholders, partners, or beneficiaries. Ownership interests owned by a nonprofit entity are considered owned by a single owner.
- An individual is considered to own the ownership interests held, directly or indirectly, by or for his or her family. Family includes only brothers and sisters (including half-brothers and half-sisters), a spouse, ancestors, and lineal descendants.
- If a person holds an option to purchase ownership interests, he or she is considered to be the owner of those ownership interests.
Originally Published By United Benefit Advisors

by admin | Oct 6, 2017 | ACA, IRS

Under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA), individuals are required to have health insurance while applicable large employers (ALEs) are required to offer health benefits to their full-time employees.
Reporting is required by employers with 50 or more full-time (or full-time equivalent) employees, insurers, or sponsors of self-funded health plans, on health coverage that is offered in order for the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to verify that:
- Individuals have the required minimum essential coverage,
- Individuals who request premium tax credits are entitled to them, and
- ALEs are meeting their shared responsibility (play or pay) obligations.
2017 Draft Forms and Instructions
Draft instructions for both the 1094-B and 1095-B and the 1094-C and 1095-C were released, as were the draft forms for 1094-B, 1095-B, 1094-C, and 1095-C. There are no substantive changes in the forms or instructions between 2016 and 2017, beyond the further removal of now-expired forms of transition relief.
In past years the IRS provided relief to employers who make a good faith effort to comply with the information reporting requirements and determined that they will not be subject to penalties for failure to correctly or completely file. This did not apply to employers that fail to timely file or furnish a statement. For 2017, the IRS has unofficially indicated that the “good faith compliance efforts” relating to reporting requirements will not be extended. Employers should be ready to fully meet the reporting requirements in early 2018 with a high degree of accuracy. There is however relief for de minimis errors on Line 15 of the 1095-C.
The IRS also confirmed there is no code for the Form 1095-C, Line 16 to indicate an individual waived an offer of coverage. The IRS also kept the “plan start month” box as an optional item for 2017 reporting.
Employers must remember to provide all printed forms in landscape, not portrait.
When? Which Employers?
Reporting will be due early in 2018, based on coverage in 2017.
For calendar year 2017, Forms 1094-C, 1095-C, 1094-B, and 1095-B must be filed by February 28, 2018, or April 2, 2018, if filing electronically. Statements to employees must be furnished by January 31, 2018. In late 2016, a filing deadline was provided for forms due in early 2017, however it is unknown if that extension will be provided for forms due in early 2018. Until employers are told otherwise, they should plan on meeting the current deadlines.
All reporting will be for the 2017 calendar year, even for non-calendar year plans. The reporting requirements are in Sections 6055 and 6056 of the ACA.
By Danielle Capilla
Originally Published By United Benefit Advisors

by admin | Sep 29, 2017 | ACA, Compliance, IRS
 In spite of the recent efforts by Congress to change or repeal the ACA, its provisions are still in effect. The IRS has issued continuing guidance on the affordability rate for coverage, the employer shared responsibility provisions and reporting, and the individual mandate provision.
In spite of the recent efforts by Congress to change or repeal the ACA, its provisions are still in effect. The IRS has issued continuing guidance on the affordability rate for coverage, the employer shared responsibility provisions and reporting, and the individual mandate provision.
IRS Released the 2018 Affordability Rate
The Internal Revenue Service released its Revenue Procedure 2017-36, which sets the affordability percentage at 9.56 percent for 2018. Under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA), an applicable large employer may be liable for a penalty if a full-time employee’s share of premium for the lowest cost self-only option offered by the employer is not affordable (for 2018, if it’s more than 9.56 percent of the employee’s household income) and the employee gets a premium tax credit for Marketplace coverage.
Because the 2018 affordability rate is lower than the 2017 affordability rate, applicable large employers may need to reduce their employees’ share of premium contributions to maintain affordable coverage. Employers should double check their anticipated 2018 premiums now to prevent the need for mid-year changes.
IRS Releases Information Letters
The IRS issued Information Letters 2017-0010, 2017-0011, 2017-0013, and 2017-0017 on the ACA’s employer shared responsibility provisions and individual mandate.
IRS Information Letters 2017-0010 and 2017-0013 explain that the ACA’s employer shared responsibility provisions continue to apply. The letters state, “The [President’s January 20, 2017] Executive Order does not change the law; the legislative provisions of the ACA are still in force until changed by the Congress, and taxpayers remain required to follow the law and pay what they may owe.” Further, the letters indicate that there are no waivers from potential penalties for failing to offer health coverage to full-time employees and their dependents.
IRS Information Letters 2017-0011 and 2017-0017 address the continued application of the ACA’s individual shared responsibility provisions. Letter 2017-0017 states, “The Executive Order does not change the law; the legislative provisions of the ACA are still in force until changed by the Congress, and taxpayers remain required to follow the law, including the requirement to have minimum essential coverage for each month, qualify for a coverage exemption for the month, or make a shared responsibility payment.”
IRS Issues Draft Forms 1094/1095
The IRS issued draft Forms 1094-B, 1095-B, 1094-C, and 1095-C for the 2017 tax year. Coverage providers use Forms 1094-B and 1095-B to report health plan enrollment. Applicable large employers use Forms 1094-C and 1095-C to report information related to their employer shared responsibility provisions under the ACA.
There are no changes to the face of draft Forms 1094-B, 1095-B, or 1095-C. The IRS made one substantive change to draft Form 1094-C. The IRS removed the line 22 box “Section 4980H Transition Relief” which was applicable to the 2015 plan year only.
By Danielle Capilla
Originally Published By United Benefit Advisors

by admin | Aug 29, 2017 | ACA, Health Plan Benchmarking
 Small employers, those with fewer than 100 employees, have a reputation for not offering health insurance benefits that are competitive with larger employers, but new survey data from UBA’s Health Plan Survey reveals they are keeping pace with the average employer and, in fact, doing a better job of containing costs.
Small employers, those with fewer than 100 employees, have a reputation for not offering health insurance benefits that are competitive with larger employers, but new survey data from UBA’s Health Plan Survey reveals they are keeping pace with the average employer and, in fact, doing a better job of containing costs.
According to our new special report: “Small Businesses Keeping Pace with Nationwide Health Trends,” employees across all plan types pay an average of $3,378 toward annual health insurance benefits, with their employer picking up the rest of the total cost of $9,727. Among small groups, employees pay $3,557, with their employer picking up the balance of $9,474 – only a 5.3 percent difference.
When looking at total average annual cost per employees for PPO plans, small businesses actually cut a better deal even compared to their largest counterparts—their costs are generally below average—and the same holds true for small businesses offering HMO and CDHP plans. (Keep in mind that relief such as grandmothering and the PACE Act helped many of these small groups stay in pre-ACA plans at better rates, unlike their larger counterparts.)
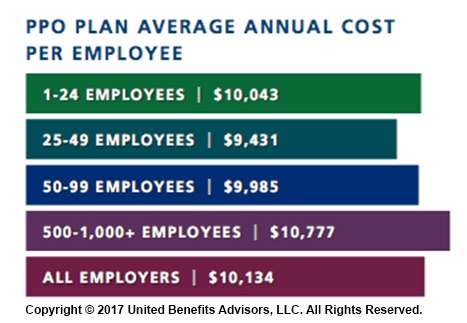
Think small businesses are cutting coverage to drive these bargains? Compared to the nations very largest groups, that may be true, but compared to average employers, small groups are highly competitive.
By Bill Olson
Originally Published By United Benefit Advisors
by admin | Aug 7, 2017 | ACA, Employee Benefits, Health & Wellness
Preexisting conditions. While it’s no doubt this term has been a hot topic in recent months—and notably misconstrued—one thing has not changed; insurers cannot deny coverage to anyone with a preexisting condition. Now that House Resolution 1628 has moved to the Senate floor, what can employers and individuals alike expect? If passed by the Senate as is and signed into law; some provisions will take place as early as 2019—possibly 2018 for special enrollment cases. It’s instrumental for companies to gear up now with a plan on how to tackle open enrollment; regardless of whether your company offers medical coverage or not.
Under the current proposed American Health Care Act (AHCA) insurance companies can:
- Price premiums based on health care status/age. The AHCA will provide “continuous coverage” protections to guarantee those insured are not charged more than the standard rate as long as they do not have a break in coverage. However, insurers will be allowed to underwrite certain policies for those that do lapse—hence charging up to 30% more for a preexisting condition if coverage lapses for more than 63 days. This is more common than not, especially for those who are on a leave of absence for illness or need extensive treatment. In addition, under current law, insurers are only allowed to charge individuals 50 and older 3 times as much than those under this age threshold. This ratio will increase 5:1 under AHCA.
- Under the ACA’s current law employers must provide coverage for 10 essential health care benefits. Under AHCA, beginning as early as 2020, insurers will allow states to mandate what they consider essential benefit requirements. This could limit coverage offered to individuals and within group plans by eliminating high cost care like mental health and substance abuse. Not that it’s likely, but large employers could eventually opt out whether they want to provide insurance and/or choose the types of coverage they will provide to their employees.
It’s important to note that states must apply for waivers to increase the ratio on insurance premiums due to age, and determine what they will cover for essential health benefits. In order to have these waivers granted, they would need to provide extensive details on how doing so will help their state and the marketplace.
So what can employers do moving forward? It’s not too soon to think about changing up your benefits package as open enrollment approaches, and educating yourself and your staff on AHCA and what resources are out there if you don’t offer health coverage.
- Make a variety of supplemental tools available to your employees. Anticipate the coming changes by offering or adding more supplemental insurance and tools to your benefits package come open enrollment. Voluntary worksite benefits, such as Cancer, Critical Illness, and Accident Insurance handle a variety of services at no out-of-pocket cost to the employer. HSA’s FSA’s and HRA’s are also valuable supplemental tools to provide your employees if you’re able to do so. Along with the changes listed above, the AHCA has proposed to also increase the contribution amounts in these plans and will allow these plans to cover Over-the-Counter (OTC) medications.
- Continue to customize wellness programs. Most companies offer wellness programs for their employees. Employers that provide this option should continue advancing in this area. Addressing the specific needs of your employees and providing wellness through various platforms will result in the greatest return on investment; and healthier employees to boot. Couple this with frequent evaluations from your staff on your current program to determine effectiveness and keep your wellness programs on point.
- Educate, educate, educate—through technology. Regardless if you employ 10 or 10,000, understanding benefit options is vital for your employees; what you have to offer them and what they may need to know on their own. Digital platforms allow individuals to manage their healthcare benefits and stay in the know with valuable resources at their fingertips. There’s no limit on the mediums available to educate your employees on upcoming changes. Partnering with a strong benefit agency to maximize these resources and keep your employees “in the know” during a constantly changing insurance market is a great way to start.

by admin | Jun 30, 2017 | ACA, Group Benefit Plans
 Earlier this month, the Department of Labor (DOL) provided an informational FAQ relating to the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (MHPAEA) and the 21st Century Cures Act (Cures Act). This is the DOL’s 38th FAQ on implementing the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) provisions and related regulations. The DOL is requesting comments on a draft model form for participants to use to request information regarding nonquantitative treatment limitations, and confirms that benefits for eating disorders must comply with the MHPAEA. Comments are due by September 13, 2017.
Earlier this month, the Department of Labor (DOL) provided an informational FAQ relating to the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (MHPAEA) and the 21st Century Cures Act (Cures Act). This is the DOL’s 38th FAQ on implementing the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) provisions and related regulations. The DOL is requesting comments on a draft model form for participants to use to request information regarding nonquantitative treatment limitations, and confirms that benefits for eating disorders must comply with the MHPAEA. Comments are due by September 13, 2017.
The MHPAEA amended various laws and regulations to provide increased parity between mental health and substance use disorder benefits and medical/surgical benefits. Generally, financial requirements such as coinsurance and copays and treatment limitations for mental health and substance use disorder benefits cannot be more restrictive than requirements for medical and surgical benefits. Regulations also provide that a plan or issuer may not impose a nonquantitative treatment limitation (NQTL) unless it is comparable and no more stringent than limitations on medical and surgical benefits in the same classification.
On December 13, 2016, President Obama signed the 21st Century Cures Act into law. The Cures Act has numerous components including directing the Secretary of Health and Human Services, Secretary of Labor, and Secretary of the Treasury (collectively, the Agencies) to issue compliance program guidance, share findings with each other, and issue guidance to group health plans and health insurance issuers to help them comply with the mental health parity rules.
The Agencies must issue guidance to group health plans and health insurance issuers; the guidance must provide information and methods that plans and issuers can use when they are required to disclose information to participants, beneficiaries, contracting providers, or authorized representatives to ensure the plans’ and issuers’ compliance with the mental health parity rules.
The Agencies must issue the compliance program guidance and guidance to group health plans and health plan issuers within 12 months after the date that the Helping Families in Mental Health Crisis Reform Act of 2016 was enacted, or by December 13, 2017.
In the June 2017 FAQ, the DOL reiterated its request for comments on the following questions, originally asked in the fall of 2016:
- Whether issuance of model forms that could be used by participants and their representatives to request information with respect to various NQTLs would be helpful and, if so, what content the model forms should include. For example, is there a specific list of documents, relating to specific NQTLs, that a participant or his or her representative should request?
- Do different types of NQTLs require different model forms? For example, should there be separate model forms for specific information about medical necessity criteria, fail-first policies, formulary design, or the plan’s method for determining usual, customary, or reasonable charges? Should there be a separate model form for plan participants and other individuals to request the plan’s analysis of its MHPAEA compliance?
- Whether issuance of model forms that could be used by States as part of their review would be helpful and, if so, what content the model form should include. For example, what specific content should the form include to assist the States in determining compliance with the NQTL standards? Should the form focus on specific classifications or categories of services? Should the form request information on particular NQTLs?
- What other steps can the Departments take to improve the scope and quality of disclosures or simplify or otherwise improve processes for requesting disclosures under existing law in connection with mental health/substance misuse disorder MH/SUD benefits?
- Are there specific steps that could be taken to improve State market conduct examinations and/or Federal oversight of compliance by plans and issuers?
The DOL is also asking for input on a draft model form that participants, enrollees, or representatives could use to request information from their health plan or issuer regarding NQTLs that may affect their MH/SUD benefits.
The Cures Act also requires that benefits for eating disorders be consistent with the requirements of MHPAEA. The DOL clarified that the MHPAEA applies to any benefits a plan or issuer may offer for treatment of an eating disorder.
By Danielle Capilla
Originally Posted By www.ubabenefits.com







