by admin | Aug 31, 2017 | Benefit Management, Flexible Spending Accounts

A health flexible spending account (FSA) is a pre-tax account used to pay for out-of-pocket health care costs for a participant as well as a participant’s spouse and eligible dependents. Health FSAs are employer-established benefit plans and may be offered with other employer-provided benefits as part of a cafeteria plan. Self-employed individuals are not eligible for FSAs.
Even though a health FSA may be extended to any employee, employers should design their health FSAs so that participation is offered only to employees who are eligible to participate in the employer’s major medical plan. Generally, health FSAs must qualify as excepted benefits, which means other nonexcepted group health plan coverage must be available to the health FSA’s participants for the year through their employment. If a health FSA fails to qualify as an excepted benefit, then this could result in excise taxes of $100 per participant per day or other penalties.
Contributing to an FSA
Money is set aside from the employee’s paycheck before taxes are taken out and the employee may use the money to pay for eligible health care expenses during the plan year. The employer owns the account, but the employee contributes to the account and decides which medical expenses to pay with it.
At the beginning of the plan year, a participant must designate how much to contribute so the employer can deduct an amount every pay day in accordance with the annual election. A participant may contribute with a salary reduction agreement, which is a participant election to have an amount voluntarily withheld by the employer. A participant may change or revoke an election only if there is a change in employment or family status that is specified by the plan.
Per the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA), FSAs are capped at $2,600 per year per employee. However, since a plan may have a lower annual limit threshold, employees are encouraged to review their Summary Plan Description (SPD) to find out the annual limit of their plan. A participant’s spouse can put $2,600 in an FSA with the spouse’s own employer. This applies even if both spouses participate in the same health FSA plan sponsored by the same employer.
Generally, employees must use the money in an FSA within the plan year or they lose the money left in the FSA account. However, employers may offer either a grace period of up to two and a half months following the plan year to use the money in the FSA account or allow a carryover of up to $500 per year to use in the following year.
By Danielle Capilla
Originally Published By United Benefit Advisors

by admin | Aug 29, 2017 | ACA, Health Plan Benchmarking
 Small employers, those with fewer than 100 employees, have a reputation for not offering health insurance benefits that are competitive with larger employers, but new survey data from UBA’s Health Plan Survey reveals they are keeping pace with the average employer and, in fact, doing a better job of containing costs.
Small employers, those with fewer than 100 employees, have a reputation for not offering health insurance benefits that are competitive with larger employers, but new survey data from UBA’s Health Plan Survey reveals they are keeping pace with the average employer and, in fact, doing a better job of containing costs.
According to our new special report: “Small Businesses Keeping Pace with Nationwide Health Trends,” employees across all plan types pay an average of $3,378 toward annual health insurance benefits, with their employer picking up the rest of the total cost of $9,727. Among small groups, employees pay $3,557, with their employer picking up the balance of $9,474 – only a 5.3 percent difference.
When looking at total average annual cost per employees for PPO plans, small businesses actually cut a better deal even compared to their largest counterparts—their costs are generally below average—and the same holds true for small businesses offering HMO and CDHP plans. (Keep in mind that relief such as grandmothering and the PACE Act helped many of these small groups stay in pre-ACA plans at better rates, unlike their larger counterparts.)
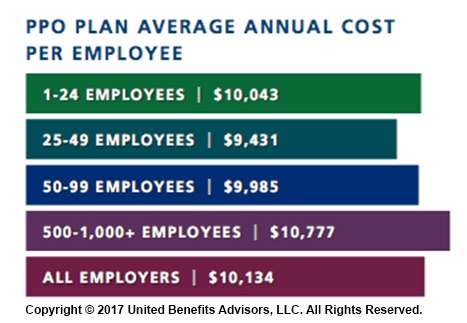
Think small businesses are cutting coverage to drive these bargains? Compared to the nations very largest groups, that may be true, but compared to average employers, small groups are highly competitive.
By Bill Olson
Originally Published By United Benefit Advisors

by admin | Aug 24, 2017 | Benefit Management, COBRA, Compliance

The Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1985 (COBRA) allows qualified beneficiaries who lose health benefits due to a qualifying event to continue group health benefits. The COBRA payment process is subject to various rules in terms of grace periods, notification, premium payment methods, and treatment of insignificant shortfalls.
Grace Periods
The initial premium payment is due 45 days after the qualified beneficiary elects COBRA. Premium payments must be made on time; otherwise, a plan may terminate COBRA coverage. Generally, subsequent premium payments are due on the first day of the month. However, under the COBRA grace period rules, premiums will still be considered timely if made within 30 days after the due date. The statutory grace period is a minimum 30-day period, but plans may allow qualified beneficiaries a longer grace period.
A COBRA premium payment is made when it is sent to the plan. Thus, if the qualified beneficiary mails a check, then the payment is made on the date the check was mailed. The plan administrators should look at the postmark date on the envelope to determine whether the payment was made on time. Qualified beneficiaries may use certified mail as evidence that the payment was made on time.
The 30-day grace period applies to subsequent premium payments and not to the initial premium payment. After the initial payment is made, the first 30-day grace period runs from the payment due date and not from the last day of the 45-day initial payment period.
If a COBRA payment has not been paid on its due date and a follow-up billing statement is sent with a new due date, then the plan risks establishing a new 30-day grace period that would begin from the new due date.
Notification
The plan administrator must notify the qualified beneficiary of the COBRA premium payment obligations in terms of how much to pay and when payments are due; however, the plan does not have to renotify the qualified beneficiary to make timely payments. Even though plans are not required to send billing statements each month, many plans send reminder statements to the qualified beneficiaries.
While the only requirement for plan administrators is to send an election notice detailing the plan’s premium deadlines, there are three circumstances under which written notices about COBRA premiums are necessary. First, if the COBRA premium changes, the plan administrator must notify the qualified beneficiary of the change. Second, if the qualified beneficiary made an insignificant shortfall premium payment, the plan administrator must provide notice of the insignificant shortfall unless the plan administrator chooses to ignore it. Last, if a plan administrator terminates a qualified beneficiary’s COBRA coverage for nonpayment or late payment, the plan administrator must provide a termination notice to the qualified beneficiary.
The plan administrator is not required to inform the qualified beneficiary when the premium payment is late. Thus, if a plan administrator does not receive a premium payment by the end of the grace period, then COBRA coverage may be terminated. The plan administrator is not required to send a notice of termination in that case because the COBRA coverage was not in effect. On the other hand, if the qualified beneficiary makes the initial COBRA premium payment and coverage is lost for failure to pay within the 30-day grace period, then the plan administrator must provide a notice of termination due to early termination of COBRA coverage.
By Danielle Capilla
Originally Published By United Benefit Advisors

by admin | Aug 21, 2017 | Benefit Management, Hot Topics, Human Resources
 In previous posts, I have talked about several aspects of strategic benefits communication. Now it’s time to put those strategies into action. As we approach enrollment season, let’s look at five key steps to ensuring this year’s open enrollment is successful for you and your employees.
In previous posts, I have talked about several aspects of strategic benefits communication. Now it’s time to put those strategies into action. As we approach enrollment season, let’s look at five key steps to ensuring this year’s open enrollment is successful for you and your employees.
1. Determine your key objectives
What do employees need to know this enrollment season? As you review your benefit plan designs, think once again about your key objectives, and for each, how you will make employees aware and keep them engaged. What are the challenges employees face when making their benefits decisions?
- Are you rolling out new medical plan options? Does this include HDHP options? An HSA? Are there changes in premiums and contribution levels?
- Are there any changes to other lines of coverage such as dental, life insurance, disability insurance?
- Are you adding new voluntary plans this year? How do they integrate with your medical plans? Do they plug gaps in high deductibles and out-of-pocket expenses? Are there existing voluntary plans with low participation?
- Are there other important topics to share with employees, like new wellness programs, or health-driven employee events?
Once you’ve gathered this information, you can develop a communication strategy that will better engage employees in the benefits decision-making process.
2. Perfect your script
What do you know about your employee demographics? Diversity doesn’t refer only to age or gender. It could mean family size, differences in physical demands of the job, income levels, or simply lifestyle. It isn’t a one-size-fits-all world anymore. As you educate employees on benefits, you will want to give examples that fit their lives.
You will also want to keep the explanations as simple as possible. Use as much plain language as you can, as opposed to “insurance speak” and acronyms. Benefit plans are already an overwhelming decision, and as we have seen in our research, employees still don’t fully understand their options.
3. Use a multi-faceted communications strategy
Sun Life research and experience has shown that the most appreciated and effective strategies incorporate multiple methodologies. One helpful tactic is to get a jump-start on enrollment communication. As enrollment season approaches, try dynamic pre-enrollment emails to all employees, using videos or brochures. Once on-site enrollment begins, set up group meetings based on employee demographics. This will arm employees with better knowledge and prepared questions for their one-to-one meeting with a benefits counselor.
Consider hard-to-reach employees as well, and keep your websites updated with helpful links and provide contacts who are available by phone for additional support.
Also, look to open enrollment as a good time to fill any employee data gaps you may have, like beneficiaries, dependents, or emergency contacts.
4. Check your tech!
We have talked in previous posts about leveraging benefits administration technology for effective communications. For open enrollment, especially when you may be introducing new voluntary insurance plans, it is important to check your technology. I recommend this evaluation take place at least 6 to 8 weeks before open enrollment if possible.
Working with your UBA advisor, platform vendor and insurance carriers, some key considerations:
- Provide voluntary product specifications from your carrier to your platform vendor. It is important to check up front that the platform can handle product rules such as issue age and age band pricing, age reduction, benefit/tier changes and guarantee issue rules. Also, confirm how the system will handle evidence of insurability processing, if needed.
- Electronic Data Interface (EDI). Confirm with your platform partner as well as insurance carriers that there is an EDI set-up process that includes testing of file feeds. This is a vital step to ensure seamless integration between your benefits administration platform, payroll and the insurance carriers.
- User Experience. Often benefits administration platforms are very effective at moving data and helping you manage your company’s benefits. As we have discussed, when it comes to your employee’s open enrollment user experience, there can be some challenges. Especially when you are offering voluntary benefits. Confirm with your vendor what, if any, decision support tools are available. Also, check with your voluntary carriers. These could range from benefit calculators, product videos, and even logic-driven presentations.
5. Keep it going
Even when enrollment season is over, ongoing benefits communications are a central tool to keeping employees informed, educated, and engaged. The small window of enrollment season may not be long enough for people to get a full grasp of their benefits needs, and often their decisions are driven by what is easily understood or what they think they need based on other people’s choices. Ongoing communications can be about specific benefits, wellness programs, or other health and benefit related items. This practice will also help new hires who need to make benefits decisions rather quickly.
In summary, work with your UBA consultant to customize benefits and enrollment communications. Leverage resources from your provider, who may, as Sun Life does, offer turnkey services that support communication, engagement, and enrollment. Explore third-party vendors that offer platforms to support the process. The whole thing can seem daunting, but following these steps and considerations will not only make the process easier for you, it will make a world of difference to your employees.
By Kevin D. Seeker
Originally Published By United Benefit Advisors

by admin | Aug 18, 2017 | COBRA, Human Resources
 The Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1985 (COBRA) allows qualified beneficiaries who lose health benefits due to a qualifying event to continue group health benefits. While some group health plans may provide COBRA continuation coverage at a reduced rate or at no cost, most qualified beneficiaries must pay the full COBRA premium. The COBRA election notice should include information about COBRA premiums.
The Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1985 (COBRA) allows qualified beneficiaries who lose health benefits due to a qualifying event to continue group health benefits. While some group health plans may provide COBRA continuation coverage at a reduced rate or at no cost, most qualified beneficiaries must pay the full COBRA premium. The COBRA election notice should include information about COBRA premiums.
For fully insured health plans, the premium is the cost to maintain the plan for similarly situated employees. For self-funded plans, the premium is the cost to maintain the plan for similarly situated employees as determined by an actuary or the past cost from the preceding determination period. The applicable premium calculation for both fully- and self-funded plans includes the cost of providing coverage to both active employees and COBRA qualified beneficiaries. All COBRA premiums must be calculated in good faith compliance with a reasonable interpretation of COBRA requirements.
Generally, COBRA payments are made on an after-tax basis. Qualified beneficiaries have 45 days after the election date to make an initial premium payment. The plan may terminate the qualified beneficiary’s COBRA rights if no initial premium payment is made before the end of the 45-day period. In addition, plans must allow monthly premium payments and cannot require payment on a quarterly basis. As established under COBRA, premiums are due on the first day of each month with a minimum 30-day grace period. A plan may terminate COBRA coverage for nonpayment or insufficient payment of premiums after the grace period.
If a qualified beneficiary makes an insignificant underpayment, then the premium payment will still satisfy the payment obligation. An underpayment is deemed insignificant if the shortfall is no greater than the lesser of $50 or 10 percent of the required amount. However, if the plan notifies the qualified beneficiary of the shortfall and grants a reasonable amount of time to correct the underpayment (usually 30 days after the notice is provided), then the qualified beneficiary is required to make the payment; otherwise, COBRA coverage may be canceled.
Fully Insured Health Plans
Generally, the applicable COBRA premium amount for fully insured plans is the insurance premium charged by the insurer. The applicable premium is based on the total cost of coverage, which includes both the employer and employee portions. The premium amount is based on the cost of coverage for similarly situated individuals who have not incurred a qualifying event.
A group health plan may charge at most 102 percent of the premium during the standard COBRA coverage period for similarly situated plan participants (100 percent of the total cost of coverage plus an additional 2 percent for administrative costs). However, the plan may increase the premium for a disabled qualified beneficiary and charge 150 percent of the applicable premium during the 11-month disability extension period (months 19 through 29). In addition, COBRA regulations permit a plan to charge a 150 percent premium to nondisabled qualified beneficiaries as long as the disabled qualified beneficiary is covered under the plan. If the disabled qualified beneficiary is no longer covered under the plan, then the remaining qualified beneficiaries may continue coverage up to 29 months at 102 percent of the cost of the plan.
If an employer maintains more than one plan, then a separate applicable premium is calculated for each plan. Also, the applicable premium for a single plan may vary due to factors such as the coverage level, the benefit package, and the region in which covered employee resides. For instance, single employees may pay a different applicable premium than employees who include their spouse on the plan. Thus, the plan may charge different premiums based on the varying coverage levels.
The most common tier structures include employee-only, employee-plus-spouse, employee-plus-children, and employee-plus-family. According to Internal Revenue Ruling 96-8, a fully insured plan that pays different premiums for individual versus family coverage must use those same premium tiers for COBRA continuation coverage. Thus, COBRA premiums are divided into multi-rate and single-rate tier structures.
By Danielle Capilla
Originally Published By United Benefit Advisors







