
by admin | Nov 9, 2017 | ACA, Human Resources, IRS

Instructions for both the 1094-B and 1095-B and the 1094-C and 1095-C were released, as were the forms for 1094-B, 1095-B, 1094-C, and 1095-C.
Reporting will be due early in 2018, based on coverage in 2017. For calendar year 2017, Forms 1094-C, 1095-C, 1094-B, and 1095-B must be filed by February 28, 2018, or April 2, 2018, if filing electronically. Statements to employees must be furnished by January 31, 2018. In late 2016, a filing deadline was provided for forms due in early 2017, however it is unknown if that extension will be provided for forms due in early 2018. Until employers are told otherwise, they should plan on meeting the current deadlines.
All reporting will be for the 2017 calendar year, even for non-calendar year plans.
The reporting requirements are in Sections 6055 and 6056 of the ACA. The major reporting requirements are:

by admin | Oct 6, 2017 | ACA, IRS

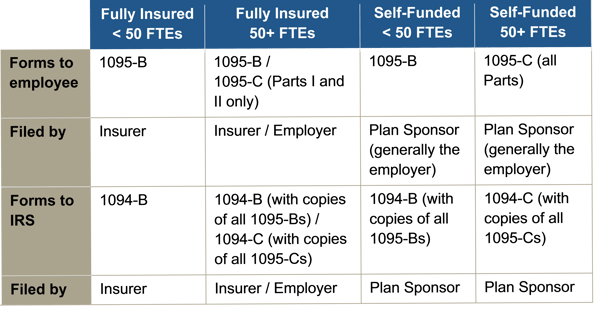
Under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA), individuals are required to have health insurance while applicable large employers (ALEs) are required to offer health benefits to their full-time employees.
Reporting is required by employers with 50 or more full-time (or full-time equivalent) employees, insurers, or sponsors of self-funded health plans, on health coverage that is offered in order for the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to verify that:
- Individuals have the required minimum essential coverage,
- Individuals who request premium tax credits are entitled to them, and
- ALEs are meeting their shared responsibility (play or pay) obligations.
2017 Draft Forms and Instructions
Draft instructions for both the 1094-B and 1095-B and the 1094-C and 1095-C were released, as were the draft forms for 1094-B, 1095-B, 1094-C, and 1095-C. There are no substantive changes in the forms or instructions between 2016 and 2017, beyond the further removal of now-expired forms of transition relief.
In past years the IRS provided relief to employers who make a good faith effort to comply with the information reporting requirements and determined that they will not be subject to penalties for failure to correctly or completely file. This did not apply to employers that fail to timely file or furnish a statement. For 2017, the IRS has unofficially indicated that the “good faith compliance efforts” relating to reporting requirements will not be extended. Employers should be ready to fully meet the reporting requirements in early 2018 with a high degree of accuracy. There is however relief for de minimis errors on Line 15 of the 1095-C.
The IRS also confirmed there is no code for the Form 1095-C, Line 16 to indicate an individual waived an offer of coverage. The IRS also kept the “plan start month” box as an optional item for 2017 reporting.
Employers must remember to provide all printed forms in landscape, not portrait.
When? Which Employers?
Reporting will be due early in 2018, based on coverage in 2017.
For calendar year 2017, Forms 1094-C, 1095-C, 1094-B, and 1095-B must be filed by February 28, 2018, or April 2, 2018, if filing electronically. Statements to employees must be furnished by January 31, 2018. In late 2016, a filing deadline was provided for forms due in early 2017, however it is unknown if that extension will be provided for forms due in early 2018. Until employers are told otherwise, they should plan on meeting the current deadlines.
All reporting will be for the 2017 calendar year, even for non-calendar year plans. The reporting requirements are in Sections 6055 and 6056 of the ACA.
By Danielle Capilla
Originally Published By United Benefit Advisors

by admin | Mar 9, 2017 | ACA, COBRA, Compliance, Human Resources, IRS
 The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) recently updated its longstanding Questions and Answers about Information Reporting by Employers on Form 1094-C and Form 1095-C that provides information on:
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) recently updated its longstanding Questions and Answers about Information Reporting by Employers on Form 1094-C and Form 1095-C that provides information on:
Generally, the Q&A describes when and how an employer reports its offers of coverage and describes the codes that employers should use when completing Form 1094-C and Form 1095-C for calendar year 2016 that are to be filed in 2017. The Q&A should be used in conjunction with the Instructions for Forms 1094-C and 1095-C which provide detailed information about completing the forms.
The updated Q&A provides information on COBRA reporting that had been left pending in earlier versions of the Q&A for the past year. UBA’s ACA Advisor “IRS Q&A About Employer Information Reporting on Form 1094-C and Form 1095-C” reviews the new information and explains other reporting obligations covered under the Q&A.
Reporting Offers of COBRA Continuation Coverage
An offer of COBRA continuation coverage that is made to a former employee due to termination of employment is not reported as an offer of coverage in Part II of Form 1095-C.
If the applicable large employer is required to complete a Form 1095-C for the former employee (because, for example, the individual was a full-time employee for one or more months of the year before terminating employment), the employer should use code 1H, No offer of coverage, on line 14 for any month that the former employee was offered COBRA continuation coverage. For those same months, the employer should use code 2A, Employee not employed during the month, on line 16 for each month in which the individual is not an employee (regardless of whether the former employee enrolled in the COBRA continuation coverage).
An employer that provides COBRA continuation coverage through a self-funded health plan generally must report that coverage for any former employee or family member who enrolls in that COBRA continuation coverage in Part III of the Form 1095-C. Also, the employer may report the coverage on Form 1095-B for any individual who was not an employee during the year and who separately elected the COBRA continuation coverage.
By Danielle Capilla, Originally Published United Benefit Advisors





