
by ckistler | Feb 23, 2021 | Human Resources, Work From Home

In the past year, many employers who would never have considered a remote work arrangement discovered that it was not only possible, but in some (or many) ways preferable to how they worked before. As a result, many employers plan on maintaining a remote workforce in some form once the pandemic is over. There’s a lesson here for all employers: the standard way of doing things is not necessarily the only or best way to do things.
As you begin the new year, it might be worth examining your HR practices and asking yourself whether the way you do things is really the best way, or just the comfortable, easy way. Look especially for areas where you’re setting unnecessary restrictions on yourself or your employees.
Job postings, for example, often have requirements that could be tossed with no loss, but a lot of gain. Does someone really need a four-year degree to do an entry level admin job? Or knowledge of how to use certain productivity tools, which can realistically be learned in a matter of hours? Restrictions such as these may be limiting your applicant pool. Other old habits may be losing you productivity and profit.
By Kyle Cupp
Originally posted on ThinkHR

by ckistler | Jan 7, 2021 | Compliance, Work From Home

According to Gallup, the number of days employees are working remotely has doubled during the pandemic. Some companies are even considering making a remote work arrangement permanent. While there are no laws that exclusively apply to remote workplaces, remote work does come with additional compliance risks. Below is our general guidance for employers.
Logging Hours and Preparing Paychecks
Make sure that employees are logging all of their time. Keep in mind that when working from home, the boundaries between work and home life are easy to blur. Employees may be racking up “off the clock” work, and even overtime, that they aren’t being paid for. While this may seem harmless enough in the moment, particularly if the employee isn’t complaining, unpaid wages can come back to bite you once the employee is on their way out the door.
Minimum Wage
Employees should be paid at least the minimum wage of the state where they physically work, whether this is a satellite office or their own home. Beyond that, it’s important to be aware that some cities and counties have even higher minimum wages than the state they are located in. In general, with most employment laws, you should follow the law that is most beneficial to the employee.
Breaks
Remote employees must take all required break and rest periods required by law, as if they were in the workplace.
Harassment Prevention Considerations
You may have employees working in a state that has a lower bar for what’s considered harassment or that requires harassment prevention training. You can find this information on the State Law pages on the HR Support Center.
Remote work also comes with additional opportunities for harassment (even if it doesn’t rise to the level of illegal harassment) such as employees wearing clothing that crosses the line into inappropriate, roommates in the background unaware that they are on camera, or visible objects that other employees may consider offensive. You can prevent these sorts of incidents by having clear, documented expectations about remote meetings, communicating those expectations to your employees, and holding everyone accountable to them. It also wouldn’t hurt to occasionally remind everyone to be mindful that they and what’s behind them are visible to coworkers when they’re on video. That said, going overboard with standards that you’re applying to employees’ private homes can cause anxiety and morale issues, so make sure your restrictions have some logical business-related explanation.
Workplace Posters
Many of the laws related to workplace posters were written decades before the internet, and so their requirements don’t always make sense given today’s technology.
The safest option to ensure you’re complying will all posting requirements in one fell swoop is to mail hard copies of any applicable workplace posters to remote employees and let them do what they like with the posters at their home office. If you have employees in multiple states, you should send each employee the required federal posters, plus any applicable to the state in which they work.
Alternatively, more risk-tolerant employers often provide these required notices and posters on a company website or intranet that employees can access. A number of newer posting laws expressly allow for electronic posting, but this option is not necessarily compliant with every posting law out there.
FMLA Eligibility
Remote employees who otherwise qualify will be eligible for leave under the federal Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) if they report to or receive work assignments from a location that has 50 or more employees within a 75-mile radius.
According to the FMLA regulations, the worksite for remote employees is “the site to which they are assigned as their home base, from which their work is assigned, or to which they report.” So, for example, if a remote employee working in Frisco, TX, reports to their company’s headquarters in Portland, OR, and that site in Portland has 65 employees working within a 75-mile radius, then the employee in Frisco may be eligible for FMLA. However, if the site in Portland has only 42 employees, then the remote employee would not be eligible for FMLA. The distance of the remote employee from the company’s headquarters is immaterial.
Verifying I-9s
In normal circumstances, the physical presence requirement of the Employment Eligibility Verification, Form I-9, requires that employers, or an authorized representative, physically examine, in the employee’s physical presence, the unexpired document(s) the employee presents from the Lists of Acceptable Documents to complete the Documents fields in Form I-9’s Section 2.
However, in March, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) temporarily suspended the physical presence requirement for employers and workplaces that are operating remotely due to COVID-19 related precautions. In other words, employers with employees taking physical proximity precautions due to COVID-19 (and operating remotely) are not required to review the employee’s identity and employment authorization documents in the employee’s physical presence. Inspection should instead be done remotely. As of the date of this newsletter, this temporary rule is still in effect.
Equipment
In some states, an employer is required either to provide employees with the tools and items necessary to complete the job or to reimburse employees for these expenses. However, workstation equipment like desks and chairs is usually not included in this category of necessary items.
That said, an employee might request a device or some form of furniture as a reasonable accommodation under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) so they can perform the essential functions of their job. In such cases, you would consider it like any other ADA request. Allowing them to take home their ergonomic office chair, for example, would probably not be an undue hardship and therefore something you should do.
Deciding Who Can Work from Home
You may offer different benefits or terms of employment to different groups of employees as long as the distinction is based on non-discriminatory criteria. For instance, a telecommuting option or requirement can be based on the type of work performed, employee classification (exempt v. non-exempt), or location of the office or the employee. You should be able to support the business justification for allowing or requiring certain groups to telecommute.
Originally posted on ThinkHR

by admin | Sep 9, 2020 | Human Resources, Work From Home

When quarantine officially came into effect, thousands of businesses with no remote work policy in place scrambled to piece together teleworking procedures robust enough to handle the complications of COVID-19. For many it was a learning process, a time of continual adjustment to find the right solutions for their organizations. Quarantine has now been in effect for several months now, and many departments have gone from growing pains to smoothly operating remotely.This means the re-emergence of non-crisis operations, like assessing your organization’s current talent and possibly filling in open positions. If your organization is at this point, you’re probably going to be conducting virtual job interviews soon—a daunting prospect for even the most seasoned HR professionals. No matter how skilled you are at conducting interviews, replicating an in-office meeting over Skype or Zoom can be a tricky needle to thread. Here are a few tips for conducting virtual interviews.
Maintain “Digital Eye Contact”
A crucial factor for in-person interviews, the importance of eye contact in an interview doesn’t disappear just because it’s over video conferencing. When maintaining eye contact in person isn’t possible, interviewers should keep their eyes trained on the camera, rather than on the candidate’s video feed. Some video conferencing software also displays an image of the person using it—I think we’ve all caught ourselves staring at our own image during a Zoom, Skype, or FaceTime, instead of the person talking. It’s easy to get distracted on remote calls, so be aware of where your eyes are focused.
Check Your Posture
As always, you’ll be a more engaging interviewer if you’re sitting up straight and exhibiting an alert, attentive posture. For virtual interviews, you should also consider leaning slightly forward to show interest in what the candidate’s saying. Leaning forward may be overkill for in-person interviews, but it’s advisable given the added barrier and distance of a video call. Just be sure to not to get too close to the camera—about an arm’s length away will suffice.
Limit Gesturing
Gesturing is an essential part of conversation, adding an important dimension to the way we communicate. While animated talking and gesturing helps provide context and additional information when we’re conversing in real life, it can be distracting on a small screen. Try to limit expressive hand motions so that the interviewee can focus on what you’re trying to communicate.
Consider On-Demand Interviewing
Despite the wide availability and ease of video conferencing, many concede it still fails to replicate the experience of an in-person interview in a satisfying way. For that reason, some companies have been experimenting with alternatives to interviews over Zoom or Skype. These include on-demand interviewing, where candidates record their responses to interview questions at their own convenience. “Instead of scheduling interviews during limited windows of time during business hours, recruiters can effectively interview larger volumes of candidates in a shorter period of time, effectively eliminating the bottleneck that often challenges that part of the hiring process.” explains HRMorning’s Tim Ilhefeld. If video conferencing interviews still aren’t cutting it for your organization, you may want to consider on-demand interviewing instead.
By Colleen Kucera, President at United Benefit Advisors
Originally posted at blog.ubabenefits.com

by admin | Aug 12, 2020 | Human Resources, Work From Home

The future of work is now. You’ve probably heard that being said since the onset of COVID-19 and the growth of remote work. Well, it’s true and as the nature of how work gets done changes, so too does the way HR’s function plays out.
In part 1, we took a look at current trends, spoke to experts and focused on the learning and development arena when it comes to the future of work. In part 2, we’ll dive into other HR specialties and consider how they are changing as well.
Talent Acquisition
In addition to talent acquisition, there are other areas that need some transformation. That includes human resources itself.
“It’s absolutely critical to put in the time to learn new things, especially when it comes to HR Technology. Don’t let fear of the unknown, or a lack of understanding about technology scare you away,” Tracie Sponenberg, Chief People Officer of the Granite Group said.
And the statistics are certainly on her side. According to a report by Harris Interactive and Eightfold.ai, those companies adopting HR are 19% more effective in reducing the time HR spends on administrative tasks.
While we’ve seen continued changes to the profession as a result of technology, we’ve also seen a real need for HR practitioners to focus on employees at the same time. HR automation/robotic process automation (RPA) provides the ability for the focus to be shared and making sure goals are met. Some of those administrative tasks include benefits management, form processing and even employee questions related to policies and procedures. Chat bots are helpful in this particular instance.
Additionally, automation with the help of provided data can reduce pain points and drive change across the business. For instance, in a manual process, there is some level of human error that can happen. While errors in automation do occur, it is at a much lower rate. Automation can be used to automate forms and workflows that avoid printing, signing and scanning. It can also automate the dissemination of those documents to ensure they are delivered to the appropriate people. And, it can also help in pulling data, filling out systems and databases and elevating manual data entry.
“If HR takes the time to automate the routine day-to-day tasks and ‘paperwork,’ we can be free to really dig into strategy and people development – coaching, training and developing our team members to be prepared for the future of work – whatever that may mean to our individual industries and companies,” Sponenberg said.
Remote Work
In addition to being prepared for the future of work as Sponenberg said, HR must keep an eye on where work is going to be happening. There aren’t many places where it’s happening in office buildings anymore. It’s happening in home offices and public spaces that can accommodate social distancing. It’s likely to stay that way as more and more workers have embraced flexible scheduling and remote work.
Remote work has quickly become a reality for many different industries, but that trend was already occurring before the pandemic. There had already been a 173% increase in people working remotely since 2005. Additionally, 75% of workers say they’re more productive at home.
Some of the reasons given include fewer distractions and less commuting. This presents a fair amount of challenge. A big one centers on engagement. Remote workers aren’t that much different from brick-and-mortar employees and the concerns are similar. Remote workers, just like those sitting in the office, are at risk for leaving the organization within the first year and even leaving to pursue other opportunities to advance. That means they need just as much attention when it comes to engagement. In some instances, more attention is necessary.
Stemming the Tide
To solve issues related to the retention of remote workers, first think about setting expectations. The whole point of remote work is not having to go into the office. As such flexible work scheduling is typically a piece of the overall remote working strategy. To be more to the point – workers probably aren’t working a 9-to-5 shift if they’re off-site. That being said, managers can set particular expectations such as times the employee is expected to be “on the clock.” Some people refer to these as “busy hours” or “office hours.” It’s during this time remote workers should be expected to be prompt in their responses to emails and phone calls as well as be available to collaborate with the team.
Secondly, these workers must be included and that requires attention-to-detail and technology. If a team is meeting at the office to discuss strategy or anything for that matter, remote workers should be allowed to participate. They should actually be expected to do so. With tools such as Zoom and Skype available, there’s no reason they should not be included in the conversation.
There is some real concern remote workers, in addition to allegedly working less, aren’t nearly as productive as their in office counterparts. Again, that’s a misconception. Look to CTrip, China’s largest travel agency. A professor from Stanford studied whether or not remote work was “beneficial or harmful for productivity.” It took two years to complete the study and what the professor found is a profound increase in productivity for a group of remote workers over their in-office counterparts.
It wasn’t all “sunshine and rainbows”, however. Those remote workers did report an increase in feeling lonely and many reported they didn’t want to work from home all the time. In the end, the recommendation was to create a hybrid of sorts; one that balanced working from home and in the office.
Words of Advice
There is no stopping the future of work. In fact, as this report has explained it’s already here. While it is a concern for every HR professional working today and those who are about to enter the practice, there are words of encouragement to be shared.

By Mason Stevenson
Originally posted on hrexchangenetwork.com

by admin | Jul 28, 2020 | COVID-19, Human Resources, Work From Home

“When people are financially invested, they want a return. When people are emotionally invested, they want to contribute.” – Simon Sinek
The COVID-19 pandemic has taught us many things. First, it has taught us that empathy and kindness goes a long way. We’ve learned that as individuals, communities, and as a nation, that we can do hard things when we work together. Finally, this pandemic has taught us that the relationship between employer and employee is a valuable one. How much the employee feels valued by their employer is called “engagement.” And this feeling of value is one that more and more companies are investing in in a post-COVID environment.
Employee engagement is when an employee feels “high levels of involvement (passion and absorption) in the work and the organization (pride and identity) as well as affective energy (enthusiasm and alertness) and a sense of self-presence.” Let’s dive in and look at some fast facts on this subject and how to increase engagement in this new workspace we have found our world occupying.
BY THE NUMBERS
- 34% of employees and 35% of employers stated they felt engaged in their work in a 2019 Gallup poll.
- 38% of employees now say they are “highly involved in, enthusiastic about and committed to their work and workplace” via a May 2020 Gallup poll.
- This is the highest reported engagement since Gallup began measuring this topic in 2000.
BOTTOM LINE
- Unengaged employees lower productivity, innovation, and the bottom line.
- Engaged employees have lower absenteeism and lower turnover.
- When an employee believes that they are being heard and seen as a valued investment, they feel empowered to do their best work.
- Teams that report being engaged in the workplace have 21% higher profitability than those who report being unengaged.
HOMESCHOOL
- One way to create engagement in the workplace is to promote learning opportunities at home for employees. This can be done in virtual workshops for remote workers.
- If a company’s investment is in learning and development, this shows the employee that their employer sees their future as important.
- Positive results of investing in workforce education include increased employee engagement, more innovation, and increased understanding of the company’s goals.
- Remote employees who participate in a company’s virtual training report that beyond the educational benefit they receive, they also feel as though they are being equipped with new skills for handling stressful situations once they are able to return to work.
RESOURCES
There are numerous blogs and articles and creative educational interaction sites to keep employees engaged and learning while remote. Below are some fun and creative sites to help you create your own engagement campaign for your organization.
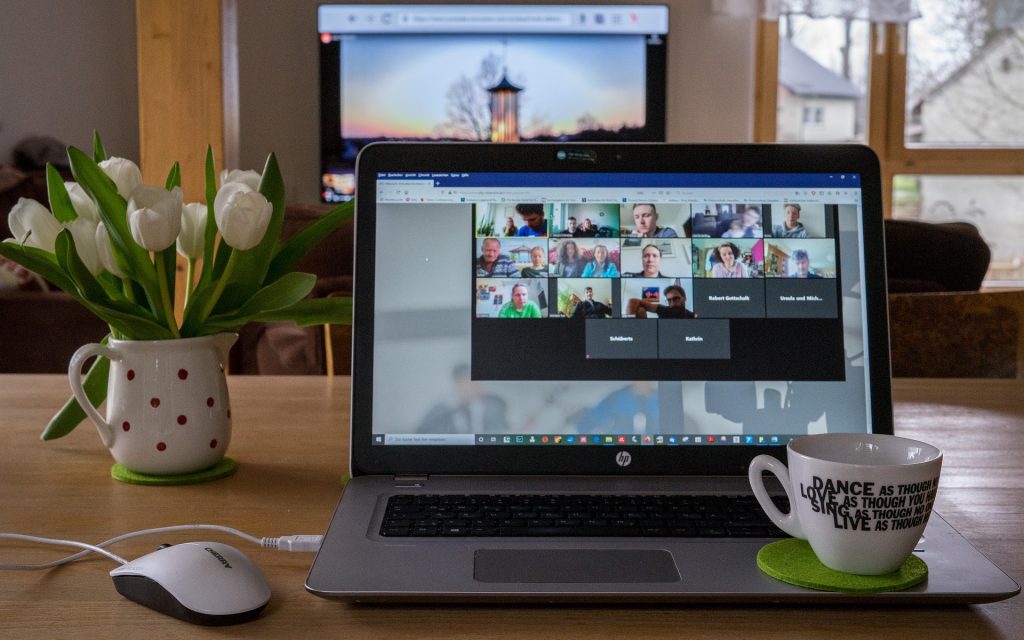
by admin | Jul 15, 2020 | Human Resources, Work From Home
 Even with video conferencing and messaging apps, fully involving remote employees in team and company meetings remains a challenge. There may be no replacing the experience of being physically in the room, but you can take steps to make meetings more productive and inclusive for remote participants.
Even with video conferencing and messaging apps, fully involving remote employees in team and company meetings remains a challenge. There may be no replacing the experience of being physically in the room, but you can take steps to make meetings more productive and inclusive for remote participants.
The most important thing to remember when “meeting” with remote employees is that you can’t conduct the meeting in the same way as you normally do when everyone is physically present. You have to find a way to replace the advantages that close proximity has, especially the ease of reading body language and picking up social cues. These, unfortunately, do not translate well over the screen or the phone. So, what can you do?
What remote employees need to fully participate in meetings is space and time to speak. You can provide this space and time in a few ways.
First, ask any physically present participants to pause for a second before jumping into the conversation. This gives remote employees time to get a word in, plus it helps counter any time delays caused by the conferencing technology. Second, whoever is leading the meeting should regularly invite remote employees to add anything if they have something to say, preferably before moving on in the agenda. Third, when possible, have one or more remote employee lead the meeting or a section on the agenda. This focuses attention on the remote speakers and can help remind everyone that the meeting isn’t just happening in one physical room. Finally, if your remote employees are located in the same workspace, occasionally setting their site as the physical meeting space can help your non-remote employees get a feel for the challenges of being remote during a meeting.
Some preliminary work before the meeting can also help make the meeting itself more efficient. First, test any systems ahead of time so that they’re working for everyone when the meeting starts. Second, email the agenda out so everyone knows what to expect. Third, assign someone in the meeting room to be the contact person that remote employees can email or message if they have questions, concerns, or issues.
After the meeting, check in with any remote employees and ask them to be candid about their experience. What worked well and what could be improved? See what you can do to accommodate them in the next meeting.
You may not be able to fully replicate the experience of physically being in the room, but taking these steps can enable remote employees to feel more involved and make the meeting itself run more smoothly.
By Kyle Cupp
Originally posted on thinkhr.com








