
by admin | Sep 9, 2024 | ACA, Compliance
 The Affordable Care Act (ACA) introduced the Medical Loss Ratio (MLR) to ensure that health insurance companies spend a significant portion of premiums on medical care and quality improvement activities rather than administrative costs and profits. When insurers fail to meet the MLR threshold, they are required to issue rebates to plan sponsors.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) introduced the Medical Loss Ratio (MLR) to ensure that health insurance companies spend a significant portion of premiums on medical care and quality improvement activities rather than administrative costs and profits. When insurers fail to meet the MLR threshold, they are required to issue rebates to plan sponsors.
Understanding MLR Rebates
The MLR mandates that health insurers spend at least a certain percentage of premium dollars on medical claims and quality improvement activities. This percentage varies depending on the type of plan. If an insurer’s medical loss ratio falls below the required threshold, they must issue a rebate to the plan sponsor, typically the employer.
Approaching Deadlines: Time to Prepare
It’s essential for employers to be aware of the MLR rebate deadlines. These deadlines vary by year, but typically, insurers have until September 30th of the following year to issue rebates for the previous year’s plan performance. For instance, rebates for 2023 plan performance are due by September 30, 2024.
What to Do with Your MLR Rebate
Employers who receive MLR rebates should carefully consider how to use the funds. While the specific use of the funds depends on the plan’s legal structure and governing documents, some common options include:
- Offsetting future premium costs: Using the rebate to reduce future premium payments.
- Funding wellness programs: Investing in employee wellness initiatives to improve overall health and productivity.
- Contributing to a health savings account (HSA): Offering additional contributions to employee HSAs to help cover healthcare costs.
- Other plan improvements: Using the rebate to enhance other plan benefits or expand coverage options.
Important Considerations:
- ERISA Compliance: If the rebate qualifies as a plan asset under ERISA, it must be used solely for the benefit of plan participants and beneficiaries.
- Documentation: Maintain proper documentation of how the rebate is used to comply with regulatory requirements.
By understanding the MLR rebate process and carefully considering how to use the funds, employers can maximize the benefits of this unexpected windfall and improve the overall health and well-being of their workforce.

by admin | Jul 9, 2024 | ACA, Compliance
 The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Trust Fund fee, often referred to as the PCORI fee, can be a source of confusion for employers offering health insurance plans. This article aims to simplify what the PCORI fee is, why it exists, and how it impacts your business.
The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Trust Fund fee, often referred to as the PCORI fee, can be a source of confusion for employers offering health insurance plans. This article aims to simplify what the PCORI fee is, why it exists, and how it impacts your business.
What is the PCORI Fee?
The PCORI fee is an annual charge levied on most health insurance plans and self-funded employer health plans. It was established by the Affordable Care Act (ACA) to fund the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI).
What Does PCORI Do?
PCORI is an independent, non-profit organization dedicated to conducting research on the effectiveness of different medical treatments and approaches. Their research helps patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers make more informed decisions about treatment options.
The IRS offers useful resources, including a chart that explains how the fees apply to different types of health coverage and arrangements.
How Much is the PCORI Fee?
The PCORI fee is calculated based on the average number of lives covered under a plan during the policy year. The fee amount is adjusted annually based on inflation in National Health Expenditures. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- For plans ending after September 30, 2023 and before October 1, 2024: The applicable dollar amount is $3.22 per covered life.
- For plans ending after September 30, 2022 and before October 1, 2023: The applicable dollar amount is $3.00 per covered life.
Who Pays the PCORI Fee?
The PCORI fee is generally paid by the issuer of a health insurance plan or the plan sponsor of a self-funded health plan. Employers offering group health plans will typically see the PCORI fee reflected in their health insurance premium statements.
When is the PCORI Fee Due?
The PCORI fee is typically due on July 31st of the year following the last day of the plan year.
Are There Any Exemptions?
Certain types of health plans are exempt from the PCORI fee, including:
- Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs)
- Certain government-funded plans (Medicare, Medicaid)
- Some limited-flexibility plans
The Bottom Line:
The PCORI fee is a relatively small annual cost that helps fund valuable research in patient-centered outcomes. Understanding the purpose and calculation of the PCORI fee can help employers better manage their health insurance expenses and contribute to the advancement of healthcare knowledge.
Additional Resources:

by admin | Nov 17, 2021 | ACA
 On September 30, 2021, the Department of Health and Human Services, the Department of Labor, and the Department of the Treasury (collectively, the Departments), along with the Office of Personnel Management (OPM), released an interim final rule (IFR) under the No Surprises Act (Act) to help protect health care consumers from surprise billing and excessive cost sharing. The IFR primarily explains the Act’s mandatory independent dispute resolution (IDR) process.
On September 30, 2021, the Department of Health and Human Services, the Department of Labor, and the Department of the Treasury (collectively, the Departments), along with the Office of Personnel Management (OPM), released an interim final rule (IFR) under the No Surprises Act (Act) to help protect health care consumers from surprise billing and excessive cost sharing. The IFR primarily explains the Act’s mandatory independent dispute resolution (IDR) process.
Background
A prior interim final rule established that, for emergency services and certain non-emergency services furnished by out-of-network (OON) providers at in-network facilities, patients will pay a cost-sharing rate similar to the in-network rate, which must be calculated based on a state All-Payer Model Agreement, specific state law, or, if neither apply, the qualifying payment amount (QPA). The QPA is generally the plan or carrier’s median contracted rate for the same or similar service in the specific geographic area.
The Act provides that the balance of the bill to be paid by the plan or carrier following patient cost sharing and any initial payment from the plan or carrier is determined between the provider (including air ambulance provider), facility, and the plan or carrier through an open negotiation period. If the parties cannot agree on a payment amount, the Act mandates a federal IDR process.
The IDR process applies only to:
- Balance billing for emergency services; cost-sharing for emergency services must be determined on an in-network basis.
- Patient copayments, co-insurance, or deductibles for emergency services and certain non-emergency services provided at an in-network facility; cannot be higher than if such services were provided by an in-network provider, and any cost-sharing obligation must be based on in-network provider rates.
- OON charges for items or services provided by an OON provider at an in-network facility; prohibited unless notice and consent given in advance. Providers and facilities must provide patients with a plain-language consumer notice explaining that patient consent is required to receive care on an OON basis before that provider can bill the patient more than in-network cost-sharing rates.
Independent Dispute Resolution
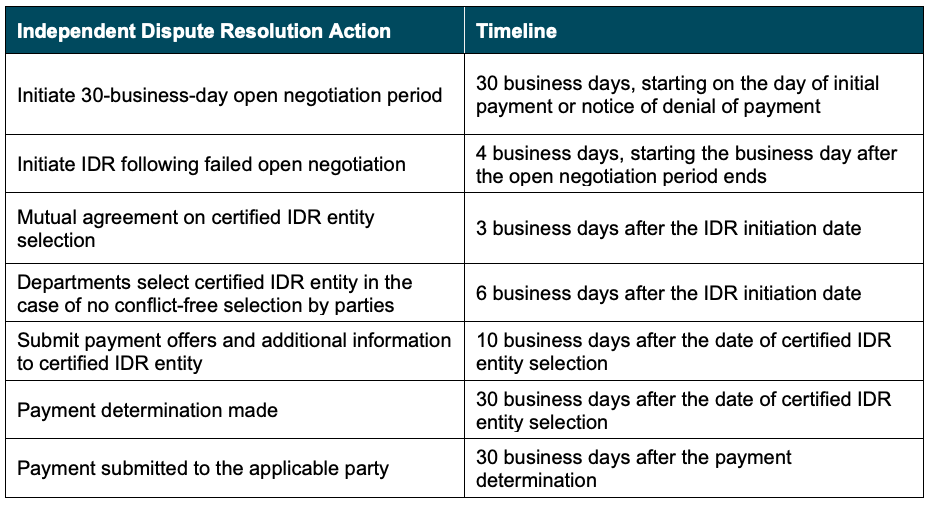
Before initiating the IDR process, disputing parties must initiate a 30-day open negotiation period. If open negotiation fails, either party may start the IDR process. If the parties cannot agree on a jointly selected certified IDR entity, or if the jointly selected certified IDR entity has a conflict of interest, the Departments will select a certified IDR entity. The parties will submit their payment offers along with supporting documentation, and the certified IDR entity will issue a binding determination by selecting one party’s offer.
When making a payment determination, certified IDR entities must assume that the QPA is the appropriate OON amount. The certified IDR entity must consider any credible permissible information submitted by a party. For the IDR entity to deviate from the offer closest to the QPA, however, any information submitted must clearly demonstrate that the value of the item or service is materially different from the QPA.
The IDR process will proceed according to the following guidelines:
Expanded External Review
Additionally, the IFR expands the scope of adverse benefit determinations eligible for external review to include determinations that involve whether a plan or issuer is complying with the surprise billing and cost-sharing protections under the No Surprises Act and its implementing regulations. In addition, under these interim final rules, grandfathered plans that are not otherwise subject to external review requirements will be subject to external review requirements for coverage decisions that involve whether a plan or issuer is complying with the surprise billing and cost-sharing protections under the No Surprises Act.
Conclusion
The regulations in the IFR become applicable to group health plans for plan and policy years beginning on or after January 1, 2022. However, the IFR is subject to a public comment period that will close in December 2021. We will continue to monitor this and other related developments under the No Surprises Act and provide ongoing updates as needed.
©2021 United Benefit Advisors, LLC. All rights reserved.

by admin | Oct 28, 2021 | ACA
 The Affordable Care Act’s employer shared responsibility provision — often called the employer mandate or “play or pay” — requires large employers to offer health coverage to their full-time employees or face a potential penalty. (Employers with fewer than 50 full-time and full-time-equivalent employees are exempt.) Large employers can avoid the risk of any play or pay penalties by offering all full-time employees at least one group health plan option that meets two standards: It provides minimum value and it is affordable.
The Affordable Care Act’s employer shared responsibility provision — often called the employer mandate or “play or pay” — requires large employers to offer health coverage to their full-time employees or face a potential penalty. (Employers with fewer than 50 full-time and full-time-equivalent employees are exempt.) Large employers can avoid the risk of any play or pay penalties by offering all full-time employees at least one group health plan option that meets two standards: It provides minimum value and it is affordable.
Minimum value means the plan’s share of total allowed costs is at least 60 percent and the plan provides substantial coverage of physician services and inpatient hospital services.
Affordable means the employee’s required contribution (payroll deduction) for self-only coverage, if elected, does not exceed a certain percentage of the employee’s household income. The affordability percentage changes slightly each year based on the law’s indexing rule. For 2021, the percentage is 9.83 percent. For 2022, however, the percentage decreases to 9.61 percent.
Although the change is minor, it means that employers need to consider whether their plan’s employee-only contribution rate will still meet the affordability standard next year.
Determining Affordability
The first step in determining whether a group health plan option is affordable is to define the employee’s “income.” Employers do not know their workers’ total household income, so the play or pay rules offer employers three optional safe harbor methods to define income using information known to the employer. Employers may use any of the safe harbor methods. They also may use different methods for different classes (such as one method for hourly employees and another method for salaried employees), provided that the chosen method is applied uniformly to all employees in the class.
The three IRS safe harbor methods are:
- Federal Poverty Line (FPL)
The FPL method is the easiest of the three methods. Multiply the mainland FPL amount for a single-member household by the affordability percentage, then divide by 12. As long as the self-only contribution rate does not exceed the resulting amount, the plan’s coverage is deemed affordable. For instance:
- 2021: ($12,760 x 9.83%)/12 = $104.52 per month
- 2022 ($12,880 x 9.61%)/12 = $103.15 per month
The FPL chart is updated every year in late January. For 2022 calendar-year health plans, the employer needs to refer to the current FPL amount ($12,880) since the new FPL amount will not be available until after the plan year starts. If the health plan year starts February 1, 2022 or later, however, the employer may refer to the new FPL amount which likely will be a little higher.
2. Rate of Pay
This is the most convenient method to define income when applied to hourly employees. Multiply the employee’s hourly rate of pay times 130 hours per month (regardless of how many hours he or she actually works), then multiply by the affordability percentage. As long as the self-only contribution rate does not exceed the resulting amount, the plan’s coverage is deemed affordable. For instance:
- 2021: ($11* x 130) x 9.83% = $140.57 per month
- 2022: ($11* x 130) x 9.61% = $137.42 per month
* Replace $11 with the hourly employee’s rate of pay.
For salaried employees, the rate of pay method is somewhat complicated so employers generally avoid using this method for non-hourly employees.
3. W-2
The W-2 method requires using current W-2 wages instead of looking back at the prior year. W-2 wages means the amount that will be reported in Box 1 of Form W-2. Pretax contributions, such as § 125 plan contributions and 401(k) or 403(b) plan deferrals, are not included in Box 1, so using the W-2 safe harbor method may understate the employee’s actual income. Coverage will be deemed affordable if, for each month of the plan year, the self-only contribution does not exceed the Box 1 amount multiplied by the affordability percentage.
Summary
Large employers can avoid the risk of potential penalties under the ACA’s play or pay rules by ensuring that they offer full-time employees at least one minimum value plan option that also is affordable. Affordable means the employee’s contribution to elect self-only coverage would not exceed a certain percentage of the employee’s income.
The percentage used to determine affordability changes from year to year is based on the law’s indexing formula. For 2021 plan years, the affordability percentage is 9.83 percent, but it decreases to 9.61 percent for 2022 plan years. Employers and their advisors will want to keep this information in mind as they finalize their group health plan offerings and employee contribution rates for 2022.
By Kathleen A. Berger, CEBS
Originally posted on Mineral

by admin | Aug 2, 2021 | ACA, Compliance, Group Benefit Plans
 On July 1, 2021, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the Department of Labor, and the Department of the Treasury (collectively, the Departments), along with the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) released an interim final rule with comment period (IFC), entitled “Requirements Related to Surprise Billing; Part I.” This rule related to Title I (the No Surprises Act) of Division BB of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021 establishes new protections from surprise billing and excessive cost-sharing for consumers receiving health care items and services. This IFC implements many of the law’s requirements for group health plans, health insurance issuers, carriers under the Federal Employees Health Benefits (FEHB) Program, health care providers and facilities, and air ambulance service providers.
On July 1, 2021, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the Department of Labor, and the Department of the Treasury (collectively, the Departments), along with the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) released an interim final rule with comment period (IFC), entitled “Requirements Related to Surprise Billing; Part I.” This rule related to Title I (the No Surprises Act) of Division BB of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021 establishes new protections from surprise billing and excessive cost-sharing for consumers receiving health care items and services. This IFC implements many of the law’s requirements for group health plans, health insurance issuers, carriers under the Federal Employees Health Benefits (FEHB) Program, health care providers and facilities, and air ambulance service providers.
Background – Surprise Billing & the Need for Greater Protections
Most group health plans and health insurance issuers that offer group or individual health insurance coverage have a network of providers and health care facilities (in-network providers) that agree to accept a specific payment amount for their services. Providers and facilities that are not part of a plan’s or issuer’s network (out-of-network providers) usually charge higher amounts than the contracted rates the plans and issuers pay to in-network providers.
When a person with health insurance coverage gets care from an out-of-network provider, their health plan or issuer usually does not cover the entire out-of-network cost, leaving the person with higher costs than if they had been seen by an in-network provider. In many cases, the out-of-network provider may bill the individual for the difference between the billed charge and the amount paid by their plan or insurance, unless prohibited by state law. This is known as “balance billing.”
A “balance bill” may come as a surprise for many people. A surprise medical bill is an unexpected bill from a health care provider or facility. This can happen when a person with health insurance unknowingly gets medical care from a provider or facility outside their health plan’s network. Surprise billing happens in both emergency and non-emergency care.
In an emergency, an individual usually goes (or is taken) to the nearest emergency department. Even if they go to an in-network hospital for emergency care, they might get care from out-of-network providers at that facility.
For non-emergency care, an individual might choose an in-network facility or an in-network provider, but not know that a provider involved in their care (for example, an anesthesiologist or radiologist) is an out-of-network provider. In both emergency and non-emergency circumstances, the person might not be able to choose the provider or ensure that all of their care is from a participating provider. In addition to getting a bill for their cost-sharing amount (like co-payments, co-insurances, and any applicable deductibles), which tends to be higher for these out-of-network services, the individual might also get a balance bill from the out-of-network provider or facility. This is especially common in the context of air ambulance services, for which individuals generally do not have the ability to choose an air ambulance provider and have little or no control over whether the provider is in-network with their plan or coverage.
When individuals do not have an opportunity to select in-network providers, their health care costs go up overall. Surprise billing is often used as leverage by providers to get higher in-network payments, which result in higher premiums, higher cost sharing for consumers, and increased health care spending overall.[1] Studies have shown that surprise bills can be high.
A recent study found that payments made to providers by people who got a surprise bill for emergency care were more than 10 times higher than those made by other individuals for the same care.
Out-of-network cost sharing and surprise bills usually do not count toward a person’s deductible and maximum out-of-pocket limit. Individuals with surprise bills may have to spend more out-of-pocket because they have to pay their out-of-network cost sharing and surprise billing amounts regardless of whether they have met their deductible and maximum out-of-pocket limits. Nine percent of individuals who got surprise bills paid more than $400 to providers, which may result in financial distress for consumers, given recent findings that show 40% of Americans struggle to find $400 to pay for an unexpected bill.[2][3],
Studies have shown that in the period from 2010-2016, more than 39% of emergency department visits to in-network hospitals resulted in an out-of-network bill, increasing to 42.8% in 2016. During the same period, the average amount of a surprise medical bill also increased from $220 to $628.[4]
Although some states have enacted laws to reduce or eliminate balance billing, these efforts have created a patchwork of consumer protections.[5] Even in a state that has enacted protections, they typically only apply to individuals enrolled in health insurance coverage, as federal law generally preempts state laws that regulate self-insured group health plans sponsored by private employers. In addition, states have limited power to address surprise bills that involve an out-of-state provider.
Summary of IFC
This IFC protects individuals from surprise medical bills for emergency services, air ambulance services provided by out-of-network providers, and non-emergency services provided by out-of-network providers at in-network facilities in certain circumstances.
If a plan or coverage provides or covers any benefits for emergency services, this IFC requires emergency services to be covered:
Without any prior authorization (i.e., approval beforehand).
Regardless of whether the provider is an in-network provider or an in-network emergency facility.
Regardless of any other term or condition of the plan or coverage other than the exclusion or coordination of benefits, or a permitted affiliation or waiting period.
Emergency services include certain services in an emergency department of a hospital or an independent freestanding emergency department, as well as post-stabilization services in certain instances.
This IFC also limits cost sharing for out-of-network services subject to these protections to no higher than in-network levels, requires such cost sharing to count toward any in-network deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums, and prohibits balance billing. These limitations apply to out-of-network emergency services, air ambulance services furnished by out-of-network providers, and certain non-emergency services furnished by out-of-network providers at certain in-network facilities, including hospitals and ambulatory surgical centers.
Cost-Sharing Amounts:
This IFC specifies that consumer cost-sharing amounts for emergency services provided by out-of-network emergency facilities and out-of-network providers, and certain non-emergency services furnished by out-of-network providers at certain in-network facilities, must be calculated based on one of the following amounts:
An amount determined by an applicable All-Payer Model Agreement under section 1115A of the Social Security Act.
If there is no such applicable All-Payer Model Agreement, an amount determined under a specified state law.
If neither of the above apply, the lesser amount of either the billed charge or the qualifying payment amount, which is generally the plan’s or issuer’s median contracted rate.
Similarly, cost-sharing amounts for air ambulance services provided by out-of-network providers must be calculated using the lesser of the billed charge or the plan’s or issuer’s qualifying payment amount, and the cost sharing requirement must be the same as if services were provided by an in-network air ambulance provider.
Balance Billing:
Under this IFC, surprise billing for items and services covered by the rule generally is not allowed.
Determining Out-of-Network Rates:
Under this IFC, the total amount to be paid to the provider or facility, including any cost sharing, is based on:
An amount determined by an applicable All-Payer Model Agreement under section 1115A of the Social Security Act.
If there is no such applicable All-Payer Model Agreement, an amount determined by a specified state law.
If there is no such applicable All-Payer Model Agreement or specified state law, an amount agreed upon by the plan or issuer and the provider or facility.
If none of the three conditions above apply, an amount determined by an independent dispute resolution (IDR) entity.
The Departments intend to issue regulations soon regarding IDR entities and the IDR process.
In limited cases, a provider or facility can provide notice to a person regarding potential out-of-network care, and obtain the individual’s consent for that out-of-network care and extra costs. However, this exception does not apply in certain situations when surprise bills are likely to happen, like for specified ancillary services connected to non-emergency care, such as anesthesiology or radiology services provided at an in-network healthcare facility.
Notice to Consumers:
This IFC requires certain health care providers and facilities to make publicly available, post on a public website, and provide to individuals a one-page notice about:
The requirements and prohibitions applicable to the provider or facility under Public Health Service Act sections 2799B-1 and 2799B-2 and their implementing regulations.
Any applicable state balance billing limitations or prohibitions.
How to contact appropriate state and federal agencies if someone believes the provider or facility has violated the requirements described in the notice.
Applicability Date & Comment Period
The regulations are generally applicable to group health plans and health insurance issuers for plan and policy years beginning on or after January 1, 2022. The HHS-only regulations that apply to health care providers, facilities, and providers of air ambulance services are applicable beginning on January 1, 2022. The OPM-only regulations that apply to carriers under the FEHB Program are applicable to contract years beginning on or after January 1, 2022. Written comments must be received by 5 p.m. 60 days after display in the Federal Register to be considered.
Visit https://www.cms.gov/files/document/cms-9909-ifc-surprise-billing-disclaimer-50.pdf to read more about the interim final rule.
Originally posted on CMS.gov
[1] Cooper, Z. et al., Surprise! Out-of-Network Billing for Emergency Care in the United States, NBER Working Paper 23623, 20173623; Duffy, E. et al., Policies to Address Surprise Billing Can Affect Health Insurance Premiums. The American Journal of Managed Care 26.9 (2020): 401-404; and Brown E.C.F., et al., The Unfinished Business of Air Ambulance Bills, Health Affairs Blog (March 26, 2021), doi: 10.1377/hblog20210323.911379, available at https://www.healthaffairs.org/do/10.1377/hblog20210323.911379/full/.
[2]Biener, A. et al., Emergency Physicians Recover a Higher Share of Charges from Out-of-network Care than from In-network Care, Health Affairs 40.4 (2021): 622-628.
[3]Board of Governors of the U.S. Federal Reserve System. Report on the Economic Wellbeing of U.S. Households in 2018. (May 2019). Available at https://www.federalreserve.gov/publications/files/2018-report-economic-well-being-us-households-201905.pdf.
[4] Sun, E.C., et al. “Assessment of Out-of-Network Billing for Privately Insured Patients Receiving Care in In-network Hospitals.” JAMA Internal Medicine, 179.11 (2019): 1543-1550. Doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.3451.
[5] States that have enacted balance billing protections include Arizona, Colorado, Delaware, Indiana, Iowa, Maine, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, New Mexico, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Texas, Vermont, and Washington.

by admin | Jul 15, 2021 | ACA, Benefit Management, Group Benefit Plans
 Do you offer coverage to your employees through a self-insured group health plan? Do you sponsor a Health Reimbursement Arrangement (HRA)? If so, do you know whether your plan or HRA is subject to the annual Patient-Centered Research Outcomes Institute (PCORI) fee?
Do you offer coverage to your employees through a self-insured group health plan? Do you sponsor a Health Reimbursement Arrangement (HRA)? If so, do you know whether your plan or HRA is subject to the annual Patient-Centered Research Outcomes Institute (PCORI) fee?
This article answers frequently-asked questions about the PCORI fee, which plans are affected, and what you need to do as the employer sponsor. PCORI fees for 2020 health plans and HRAs are due August 2, 2021.
What is the PCORI fee?
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) created the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute to study clinical effectiveness and health outcomes. To finance the nonprofit institute’s work, a small annual fee is charged on health plans.
Most employers do not have to take any action because most employer-sponsored health plans are provided through group insurance contracts. For insured plans, the carrier is responsible for the PCORI fee and the employer has no duties.
If, however, you are an employer that self-insures a health plan or an HRA, it is your responsibility to determine whether PCORI applies and, if so, to calculate, report, and pay the fee.
The annual PCORI fee is equal to the average number of lives covered during the health plan year, multiplied by the applicable dollar amount:
- If the plan year end date was between January 1 and September 30, 2020: $2.54.
- If the plan year end date was between October 1 and December 31, 2020: $2.66.
Payment is due by July 31 following the end of the calendar year in which the plan year ended. If July 31 falls on a weekend, the due date is the next following business day. So the due date for plan years ending in 2020 is August 2, 2021.
Does the PCORI fee apply to all health plans?
The fee applies to all health plans and HRAs, excluding the following:
- Plans that primarily provide “excepted benefits” (e.g., stand-alone dental and vision plans, most health flexible spending accounts with little or no employer contributions, and certain supplemental or gap-type plans).
- Plans that do not provide significant benefits for medical care or treatment (e.g., employee assistance, disease management, and wellness programs).
- Stop-loss insurance policies.
- Health savings accounts (HSAs).
The IRS provides a helpful chart indicating the types of health plans that are, or are not, subject to the PCORI fee.
If I have multiple self-insured plans, does the fee apply to each one?
Yes. For instance, if you self-insure one medical plan for active employees and another medical plan for retirees, you will need to calculate, report, and pay the fee for each plan. There is an exception, though, for “multiple self-insured arrangements” that are sponsored by the same employer, cover the same participants, and have the same plan year. For example, if you self-insure a medical plan with a self-insured prescription drug plan, you would pay the PCORI fee only once with respect to the combined plan.
Does the fee apply to HRAs?
Yes. The PCORI fee applies to HRAs, which are self-insured health plans, although the fee is waived in some cases. If you self-insure another plan, such as a major medical or high deductible plan, and the HRA is merely a component of that plan, you do not have to pay the PCORI fee separately for the HRA. In other words, when the HRA is integrated with another self-insured plan, you only pay the fee once for the combined plan.
On the other hand, if the HRA stands alone, or if the HRA is integrated with an insured plan, you are responsible for paying the fee for the HRA.
What about QSEHRAs? Does the fee apply?
Yes. A Qualified Small Employer Health Reimbursement Arrangement (QSEHRA) is special type of tax-advantaged arrangement that allows small employers to reimburse certain health costs for their workers. Although a QSEHRA is not the same as an HRA, and the rules applying to each type are very different, a QSEHRA is a self-insured health plan for purposes of the PCORI fee. The IRS provides guidance confirming that small employers that offer QSEHRAs must calculate, report and pay the PCORI fee.
What about ICHRAs and EBHRAs? Does the fee apply?
An Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangement (ICHRA) is a new type of tax-advantaged arrangement, first offered in 2020, that allows employers to reimburse certain health costs for their workers. The IRS has not provided specific guidance regarding ICHRAs and the PCORI fee, but it appears the fee applies since an ICHRA is a self-insured health plan.
An Excepted Benefits Health Reimbursement Arrangement (EBHRA) also is a self-insured health plan but it is limited to “excepted benefits,” such as dental and vision care costs. So the PCORI fee does not apply to EBHRAs.
Can I use ERISA plan assets or employee contributions to pay the fee?
No. The PCORI fee is an employer expense and not a plan expense, so you cannot use ERISA plan assets or employee contributions to pay the fee. (An exception is allowed for certain multiemployer plans (e.g., union trusts) subject to collective bargaining.) Since the fee is paid by the employer as a business expense, it is tax deductible.
How do I calculate the fee?
Multiply $2.54 or $2.66 (depending on the date the plan year ended in 2020) times the average number of lives covered during the plan year. “Covered lives” are all participants, including employees, dependents, retirees, and COBRA enrollees.
You may use any one of the following counting methods to determine the average number of lives:
- Average Count Method: Count the number of lives covered on each day of the plan year, then divide by the number of days in the plan year.
- Snapshot Method: Count the number of lives covered on the same day each quarter, then divide by the number of quarters (e.g., four). Or count the lives covered on the first of each month, then divide by the number of months (e.g., 12). This method also allows the option — called the “snapshot factor method” — of counting each primary enrollee (e.g., employee) with single coverage as “1” and counting each primary enrollee with family coverage as “2.35.”
- Form 5500 Method: Add together the “beginning of plan year” and “end of plan year” participant counts reported on the Form 5500 for the plan year. There is no need to count dependents using this method since the IRS assumes the sum of the beginning and ending of year counts is close enough to the total number of covered lives. If the plan is employee-only without dependent coverage, divide the sum by 2. (If Form 5500 for the plan year ending in 2020 is not filed by August 2, 2021, you cannot use this counting method.)
- Any Reasonable Method: This method is an exception allowed only for plan years ending between October 1, 2019 and September 30, 2020. Typically, only the first three methods above are allowed. The IRS recognizes, however, that plan sponsors may not have tracked counts using those methods since the fee had expired before it was unexpectedly reinstated by Congress in late 2019. In Notice 2020-44, the IRS explains that plan sponsors may use any reasonable method to determine the plan’s average number of covered lives
For an HRA, QSEHRA or ICHRA, count only the number of primary participants (employees) and disregard any dependents.
How do I report and pay the fee?
Use Form 720, Quarterly Excise Tax Return, to report and pay the annual PCORI fee. Report all information for self-insured plan(s) with plan year ending dates in 2020 on the same Form 720. Do not submit more than one Form 720 for the same period with the same Employer Identification Number (EIN), unless you are filing an amended return.
The IRS provides Instructions for Form 720. Here is a quick summary of the items for PCORI:
- Fill in the employer information at the top of the form.
- In Part II, complete line 133(c) and/or line 133(d), as applicable, depending on the plan year ending date(s). If you are reporting multiple plans on the same line, combine the information.
- In Part II, complete line 2 (total).
- In Part III, complete lines 3 and 10.
- Sign and date Form 720 where indicated.
- If paying by check or money order, also complete the payment voucher (Form 720-V) provided on the last page of Form 720. Be sure to fill in the circle for “2nd Quarter.” Refer to the Instructions for mailing information.
Caution! Before taking any action, confirm with your tax department or controller whether your organization files Form 720 for any purposes other than the PCORI fee. For instance, some employers use Form 720 to make quarterly payments for environmental taxes, fuel taxes, or other excise taxes. In that case, do not prepare Form 720 (or the payment voucher), but instead give the PCORI fee information to your organization’s tax preparer to include with its second quarterly filing.
Summary
If you self-insure one or more health plans or sponsor an HRA, you may be responsible for calculating, reporting, and paying annual PCORI fees. The fee is based on the average number of lives covered during the health plan year. The IRS offers a choice of different counting methods to calculate the plan’s average covered lives. Once you have determined the count, the process for reporting and paying the fee using Form 720 is fairly simple. For plan years ending in 2020, the deadline to file Form 720 and make your payment is August 2, 2021.
By Kathleen A. Berger, CEBS
Originally posted on Trustmineral.com

 The Affordable Care Act (ACA) introduced the Medical Loss Ratio (MLR) to ensure that health insurance companies spend a significant portion of premiums on medical care and quality improvement activities rather than administrative costs and profits. When insurers fail to meet the MLR threshold, they are required to issue rebates to plan sponsors.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) introduced the Medical Loss Ratio (MLR) to ensure that health insurance companies spend a significant portion of premiums on medical care and quality improvement activities rather than administrative costs and profits. When insurers fail to meet the MLR threshold, they are required to issue rebates to plan sponsors.





 On July 1, 2021, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the Department of Labor, and the Department of the Treasury (collectively, the Departments), along with the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) released an interim final rule with comment period (IFC), entitled “Requirements Related to Surprise Billing; Part I.” This rule related to Title I (the No Surprises Act) of Division BB of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021 establishes new protections from surprise billing and excessive cost-sharing for consumers receiving health care items and services. This IFC implements many of the law’s requirements for group health plans, health insurance issuers, carriers under the Federal Employees Health Benefits (FEHB) Program, health care providers and facilities, and air ambulance service providers.
On July 1, 2021, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the Department of Labor, and the Department of the Treasury (collectively, the Departments), along with the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) released an interim final rule with comment period (IFC), entitled “Requirements Related to Surprise Billing; Part I.” This rule related to Title I (the No Surprises Act) of Division BB of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021 establishes new protections from surprise billing and excessive cost-sharing for consumers receiving health care items and services. This IFC implements many of the law’s requirements for group health plans, health insurance issuers, carriers under the Federal Employees Health Benefits (FEHB) Program, health care providers and facilities, and air ambulance service providers.
 Do you offer coverage to your employees through a self-insured group health plan? Do you sponsor a Health Reimbursement Arrangement (HRA)? If so, do you know whether your plan or HRA is subject to the annual Patient-Centered Research Outcomes Institute (PCORI) fee?
Do you offer coverage to your employees through a self-insured group health plan? Do you sponsor a Health Reimbursement Arrangement (HRA)? If so, do you know whether your plan or HRA is subject to the annual Patient-Centered Research Outcomes Institute (PCORI) fee?