
by admin | Nov 9, 2023 | Compliance
 ADJUSTED CIVIL PENALTIES
ADJUSTED CIVIL PENALTIES
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has recently announced adjustments to civil penalties related to violations of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), the Affordable Care Act (ACA), and the Medicare Secondary Payer (MSP) rules. These penalty adjustments take into account inflation and are applicable to violations that occurred on or after November 2, 2015, and for which penalties are assessed on or after October 6, 2023.
HIPAA, which focuses on privacy and security rules, categorizes penalties based on the level of intention behind the violation.
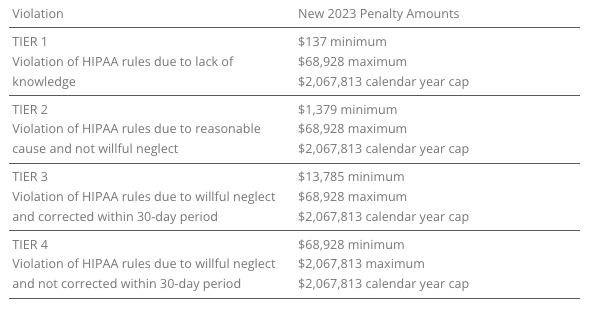
The maximum penalty for failing to provide an SBC to eligible individuals before enrollment (or re-enrollment) in a group health plan has increased from $1,264 to $1,362.
The Medicare Secondary Payer (MSP) rules prevent employers from providing incentives to Medicare beneficiaries to waive or terminate primary group health plan coverage. The maximum penalty for not complying with MSP rules has increased to $11,162 from $10,360. Furthermore, the maximum penalty for failing to inform HHS when a group health plan is or was primary to Medicare has risen to $1,428 from $1,325.
EMPLOYER CONSIDERATIONS
To avoid these penalties, employers should carefully review their plan documents and operations to ensure compliance with the HHS-related requirements.
2023 LIMITS ANNOUNCED FOR HDHPS, HSAS, FSAS
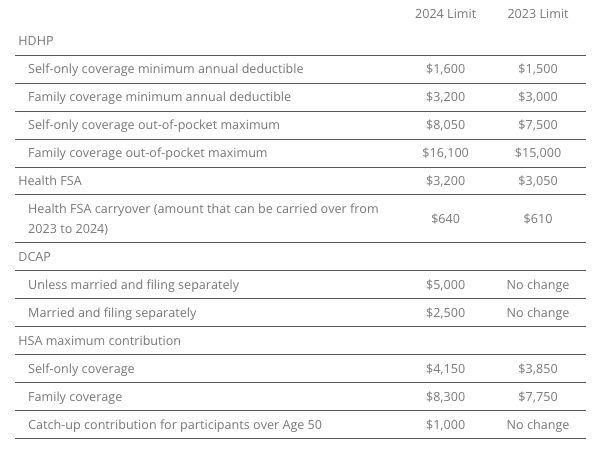
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) announced the new limits for high-deductible health plans (HDHPs), health savings accounts (HSAs), and Dependent Care Assistance Plans (DCAPs), and health flexible spending arrangements (FSAs). The new limits take effect beginning January 1, 2024.
MINNESOTA PAID SICK AND SAFE LEAVE LAW
Minnesota has recently passed a statewide paid sick and safe time leave law set to take effect on January 1, 2024. This law mirrors similar laws already in place in four Minnesota cities—Minneapolis, St. Paul, Duluth, and Bloomington. The key feature of the state law is the “front loading method,” which allows employers to provide employees with 48 hours of earned sick and safe time (ESST) in the first year of employment. Employers can pay out the value of unused hours at the end of the year and avoid carrying over unused hours into the next year.
EMPLOYER CONSIDERATIONS
This option provides flexibility for employers in managing employee leaves of absence. Local ordinances are not preempted by the state law, and employers must follow the most protective provisions of the state or local ordinances. The determination of which is more protective depends on whether more leave or monetary benefits are considered more beneficial for employees. See the FAQs for more information.
CALIFORNIA EXPANDS PAID SICK LEAVE
On October 4, 2023, Governor Gavin Newsom signed Senate Bill No. 616 into law, amending California’s paid sick leave regulations. The key changes introduced by SB 616 are:
- Starting January 1, 2024, California employers must provide employees with five days or 40 hours of paid sick leave, an increase from the previous requirement of three days or 24 hours.
- Employers can continue to provide paid sick leave at a rate of one hour for every 30 hours worked. If they use a different accrual rate, employees must accrue a minimum of 40 hours by their 200th day of employment and at least 24 hours by the 120th day of employment. Employers can also front load the entire paid sick leave amount.
- Employers may still limit the annual use of paid sick leave, but SB 616 increases the annual usage cap from 24 hours to 40 hours. The bill allows employers to cap paid sick leave accrual at 80 hours or 10 days, up from the previous limit of 48 hours or six days.
- While SB 616 continues to exempt certain collective bargaining agreement employees from the accrual requirement, it extends some provisions of California’s paid sick leave law to non-construction industry collective bargaining agreement employees. These employees may use paid sick leave for specific reasons, such as health-related issues or domestic violence, without facing retaliation. Employers cannot require these employees to find replacement workers when using sick days.
EMPLOYER CONSIDERATIONS
To comply with SB 616, employers are advised to review and update their paid sick leave policies to align with the new requirements and usage caps. Human resources and managers should also ensure proper implementation and adherence to the law.
QUESTION OF THE MONTH
Q: My wife and I work in the same small company. Is having her on my plan as spouse allowed? Can we both contribute separately from our own paychecks into our own Health Savings Account (HSA)? Or does it need to be my deduction only since I am the policy holder?
A: Yes, each spouse can have an HSA. The family limit, however, is divided between the two spouses, meaning the contributions to both HSAs combined cannot exceed the family HSA contribution limit.
Answers to the Question of the Week are provided by Kutak Rock LLP. Kutak Rock provides general compliance guidance through the UBA Compliance Help Desk, which does not constitute legal advice or create an attorney-client relationship. Please consult your legal advisor for specific legal advice.
| This information is general in nature and provided for educational purposes only. It is not intended to provide legal advice. You should not act on this information without consulting legal counsel or other knowledgeable advisors. |
| ©2023 United Benefit Advisors |

by admin | Aug 24, 2023 | Compliance
 PROPOSED CHANGES TO SHORT-TERM, LIMITED-DURATION INSURANCE
PROPOSED CHANGES TO SHORT-TERM, LIMITED-DURATION INSURANCE
On July 7, 2023, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the Department of Labor (DOL), and the Department of the Treasury proposed changes to modify the definition of short-term, limited-duration insurance (STLDI) and the conditions for fixed indemnity insurance to be considered an excepted benefit. The proposal also asks for comments on specified disease plans and level-funded plans. The proposal looks to clarify the tax treatment of certain benefit payments under group health plans.
Short-term, limited-duration insurance is meant to fill temporary gaps in coverage during transitions. The proposal suggests limiting the initial contract period to no more than three months and the maximum coverage period to no more than four months, including renewals. This change aims to differentiate STLDI from comprehensive coverage and reduce financial risk for individuals using it as a long-term alternative.
The proposal also forbids the same issuer from issuing multiple STLDI policies to the same policyholder within a year (known as “stacking”). STLDI sales mainly occur through group trusts or associations, and the proposal clarifies that such sales are not group coverage for federal law purposes.
Fixed indemnity plans provide income replacement rather than full medical coverage. The proposed regulations look to clarify that this coverage should not pay benefits on a per-service basis, to avoid mimicking comprehensive coverage without providing the same consumer protections. The proposal also includes payment standards for fixed indemnity plans and clarifies that such coverage must be offered independently without coordination with other health plans.
Consumer notices would provide clearer information on the differences between STLDI, fixed indemnity excepted benefits coverage, and comprehensive coverage.
PCORI FEE PAYMENT
Plan sponsors of self-funded medical plans, including health reimbursement arrangements (HRAs), were required to report and pay fees to the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) by July 31. This fee on group health plans was created through the 2010 Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA).
Research funded by PCORI concentrates on healthcare challenges faced by families every day, including cancer, diabetes, maternal mortality, opioid addiction, mental health, and equitable access to care, among many others.
If you believe you should have paid this fee, contact your broker for information, and access additional information including Form 720 for to submit the fee.
GROUP HEALTH PLANS ENCOURAGED TO EXPAND ENROLLMENT PERIOD FOR INDIVIDUALS LOSING MEDICAID AND CHIP
In a letter dated July 20, 2023, from the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to employers, plan sponsors, and issuers, the Biden Administration encouraged these entities to offer additional enrollment opportunities in group health plans for employees and their dependents who are losing coverage under Medicaid.
The U.S. is experiencing a health coverage transition due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The pause on Medicaid coverage verifications and terminations ended on March 31, 2023, and state Medicaid agencies are now resuming regular eligibility and enrollment operations, which include renewing coverage for eligible individuals and terminating coverage for those no longer eligible.
According to a Department of Health & Human Services report, about 3.8 million individuals who lose Medicaid eligibility could be eligible for employment-based coverage. The Administration believes that many people may need more than the typical 60-day window after losing Medicaid or Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) coverage to apply for and enroll in other coverage, especially considering the unique circumstances surrounding the resumption of Medicaid and CHIP renewals.
To address this concern, CMS has announced a temporary special enrollment period on HealthCare.gov. Marketplace-eligible individuals who lose Medicaid or CHIP coverage and come to HealthCare.gov between March 31, 2023, and July 31, 2024, will be able to enroll. Employers are encouraged to follow suit by expanding special enrollment periods for individuals losing Medicaid or CHIP coverage. These changes would require a plan amendment and approval from the insurance carrier.
Employers interested in sharing this with employees should provide information about Medicaid and CHIP renewals to employees and encourage them to update their contact information with their state agency, using CMS resources available at www.medicaid.gov/unwinding. Employers can voluntarily open enrollment in their employment-based plan for those losing Medicaid or CHIP coverage.
PROPOSED RULES MAY IMPACT MHPAEA AND NQTL DATA COLLECTION
On July 25, 2023, the U.S. Departments of Treasury, Labor, and Health and Human Services (the “Departments”) issued a comprehensive set of guidelines to help employers comply with the requirements of the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (MHPAEA). The guidelines, including definitions and examples, emphasize the importance of access to mental health and substance abuse treatment, and data collection for the production of analysis reports.
A new rule focuses on networks having an adequate number of appropriate providers. Low reimbursement rates for behavioral health care providers compared to primary care providers negatively impact access to care. Plans must collect and analyze network adequacy data and provider reimbursement rates to address this issue.
The guidelines also establish specific content and delivery requirements for the non-quantitative treatment limitations (NQTL) comparative analysis and set minimum data collection standards. The Departments expressed dissatisfaction with the current state of plans compliance with the NQTL analysis requirements and aim to bridge the gap with the proposed regulations.
These regulations are still in the proposal stage, and incoming comments may lead to modifications. Employers should review the guidelines with their brokers, paying particular attention to their network providers, as access to mental health and substance abuse disorder care is a top priority.
QUESTION OF THE MONTH
Q: My staff count has been fluctuating around 50 for some time. How do I know if or when I need to offer health insurance to my employees?
A: Whether an employer is an applicable large employer (ALE) is determined each calendar year, and generally depends on the average size of an employer’s workforce during the prior year.
If an employer has fewer than 50 full-time employees, including full-time equivalent employees, on average during the prior year, the employer is not an ALE for the current calendar year and therefore not subject to the employer shared responsibility provisions or the reporting provisions for the current year.
If an employer has at least 50 full-time employees, including full-time equivalent employees, on average during the prior year, the employer is an ALE for the current calendar year, and is therefore subject to the employer shared responsibility provisions and the reporting provisions.
| This information is general in nature and provided for educational purposes only. It is not intended to provide legal advice. You should not act on this information without consulting legal counsel or other knowledgeable advisors. |
|
©2023 United Benefit Advisors |

by admin | Jun 22, 2023 | Compliance
 CLAIMS SUBSTANTIATION FOR PAYMENT OR REIMBURSEMENT OF MEDICAL AND DEPENDENT CARE EXPENSES
CLAIMS SUBSTANTIATION FOR PAYMENT OR REIMBURSEMENT OF MEDICAL AND DEPENDENT CARE EXPENSES
A memorandum released by the IRS Chief Counsel responds to a request for assistance regarding the reimbursement of medical and dependent care expenses. Addressed is whether reimbursements of medical expenses from a health flexible spending arrangement (FSA) provided in a cafeteria plan should be included in an employee’s gross income if the expenses are not properly substantiated. The conclusion is that if any expenses, including those below a certain threshold, are not substantiated, the reimbursements must be included in the employee’s gross income.
The second issue concerns the method of substantiation for expenses. The document examines different scenarios, such as self-certification, sampling of expenses, not requiring substantiation for small amounts, and not requiring substantiation for charges with favored providers. The conclusion is that if a cafeteria plan does not require proper substantiation, it fails to operate in accordance with the regulations and the benefits must be included in the employee’s gross income.
Read the full description of the scenarios, an analysis of the relevant laws and regulations on income tax withholding and the regulations for cafeteria plans and substantiation of expenses.
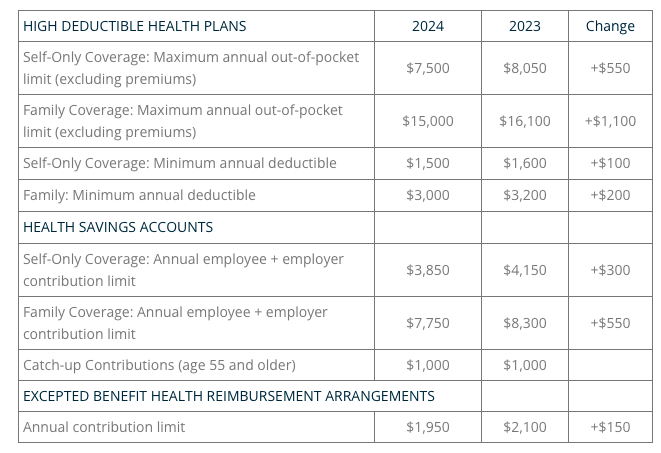
2024 LIMITS ANNOUNCED FOR HDHPS, HSAS, AND EXCEPTED BENEFIT HRAS
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) announced the new limits for high-deductible health plans (HDHPs), health savings accounts (HSAs), and excepted benefit health reimbursement arrangements (EBHRAs).
The new limits for both HDHPs and HSAs will go into effect for calendar year 2024 while the HRA limits will go into effect for plan years beginning in 2024.
PREVENTIVE HEALTH SERVICES COVERAGE AND THE BRAIDWOOD DECISION
On May 15, 2023, the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals temporarily halted the enforcement of a district court’s ruling in the Braidwood Management Inc. v. Becerra case. The district court had invalidated a portion of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) that required coverage of certain preventive care services without cost-sharing, citing religious beliefs as the reason for the violation. The Justice Department appealed the decision, and while the appeal is ongoing, the Fifth Circuit issued an administrative stay, effectively reinstating the ACA’s requirement for full coverage of preventive care. A final decision from the Fifth Circuit is expected later this year.
The Braidwood decision concluded that the determination of certain preventive care requirements under the ACA violated the Appointments Clause of the United States Constitution. These requirements are typically based on recommendations from entities such as the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) and the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA). However, the court’s ruling specifically targeted recommendations made by the USPSTF after March 23, 2010.
The Departments of Labor, Health and Human Services, and the Treasury, responsible for enforcing the preventive service coverage requirements, have appealed the court’s decision. The Departments have issued an FAQ clarifying the impact of the Braidwood ruling, stating that it only applies to services recommended by the USPSTF after March 23, 2010, and does not affect guidance related to immunizations recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) or comprehensive guidance supported by the HRSA. State laws may still require coverage of USPSTF-recommended services.
Although the Braidwood decision suspends the enforcement of certain preventive care coverage, it is expected that few employers will make significant changes until the outcome of the case is determined through the appeals process.
QUESTION OF THE MONTH
Q: Throughout the pandemic, our company’s group health plan has covered COVID-19 testing and vaccines at no cost to plan participants. Is this still required now that the public health emergency has ended?
A: During the COVID-19 public health emergency (PHE), group health plans had to cover COVID-19 testing and vaccines without cost-sharing or restrictions. Coverage requirements for diagnostic testing no longer apply after the PHE, but plans are encouraged to continue providing coverage at no cost. However, plans may choose not to cover tests or impose cost-sharing. The requirement to cover COVID-19 vaccines as a preventive service remains in effect for non-grandfathered health plans, but coverage for out-of-network providers is no longer mandatory if there is an in-network option. Plans are encouraged to notify participants of any changes to COVID-related coverage, and modifications must be disclosed at least 60 days in advance, except for changes that revert to pre-PHE conditions.
© UBA. All rights reserved.
| This information is general in nature and provided for educational purposes only. It is not intended to provide legal advice. You should not act on this information without consulting legal counsel or other knowledgeable advisors. |

 ADJUSTED CIVIL PENALTIES
ADJUSTED CIVIL PENALTIES


