by admin | Oct 30, 2025 | Custom Content, Employee Benefits, Health Care Costs
 No doubt about it, prescriptions are expensive. While this may not be a big worry when you’re young and healthy, the costs can add up quickly if you’re diagnosed with a chronic condition or need an expensive drug. Whether you take medications regularly or for an occasional illness, it pays to know how to save money on prescriptions.
No doubt about it, prescriptions are expensive. While this may not be a big worry when you’re young and healthy, the costs can add up quickly if you’re diagnosed with a chronic condition or need an expensive drug. Whether you take medications regularly or for an occasional illness, it pays to know how to save money on prescriptions.
Did You Know?
Drug costs are a primary driver of rising healthcare expenses for both employers and employees. Prescription drug spending is consistently growing at a faster rate than overall healthcare costs, with a steady increase of 6.8%. As the fastest-growing part of benefits plans, these costs will continue to climb with new pharmaceutical innovations.
For years in the U.S., cost has been a significant obstacle to sticking with medications with up to 3 in 10 people reporting that they do not take their medications as prescribed.
The Rising Cost of Prescriptions
Historically, prescription drug costs have outpaced total healthcare costs. The following chart highlights this trend from 2019 to 2024. 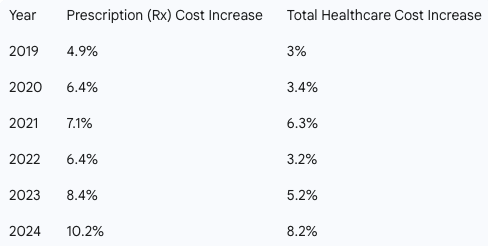
Prescription drug costs can put a strain on your budget, but with a little research and the right questions, you can reduce expenses without sacrificing your health.
Here are expert-backed strategies to help you save on your medications:
-
-
- Ask About a Generic Drug – Get the same quality and active ingredient as you’d find in a brand name, for less money.
- Save Money with a Pill Splitter – If your prescription comes in a higher dose that can be safely split, you get 2 doses for the price of 1.
- Consider a Combo Pill – Combining two drugs into one pill can help you avoid paying separate copays or coinsurance. Ask if a combo pill is an option for you.
- Buy in Bulk – Opt for a mail-order pharmacy to get a 90-day supply of your meds instead or a 30-day supply. This can often reduce your copay and overall cost.
- Make a List and Check it Twice – Check the list of preferred medications (a.k.a. “the formulary”), which tend to cost less.
- Find Out if You Still Need That Medication – If you’ve been taking the same medication for years, it’s worth checking in with your doctor to see if you still need it. Or if you’ve made a lifestyle change, it may reduce your need for certain medications. It never hurts to ask your doctor.
-
-
-
-
-
The medicines prescribed by your doctor are essential to your good health. With some savvy shopping, you can use the money you save on the things you enjoy!

by admin | Oct 21, 2025 | Employee Benefits, Open Enrollment
 Open enrollment is a hectic and critical period for employers that often brings a risk of compliance errors. These mistakes can confuse employees and cause missed benefits, while also exposing employers to legal risks.
Open enrollment is a hectic and critical period for employers that often brings a risk of compliance errors. These mistakes can confuse employees and cause missed benefits, while also exposing employers to legal risks.
This article highlights five common compliance pitfalls to avoid during open enrollment:
- Ineffective Communication of Benefit Changes – Benefit offerings often change annually due to plan design updates or regulatory mandates. Employers must clearly notify employees of any changes, including cost-sharing adjustments and new benefits, well before open enrollment. Using multiple communication channels and simple explanations helps employees make informed choices. Updates should also be reflected in required plan documents like the Summary Plan Description (SPD) or Summary of Material Modifications (SMM).
- Overlooking Election Deadlines
– Open enrollment periods should end well before the new plan year to allow orderly processing and compliance with tax laws. Employees’ benefit elections under Section 125 cafeteria plans are typically irrevocable for the plan year unless a qualifying life event occurs. Clear communication and encouraging early enrollment help prevent late or mistaken elections, which are difficult to correct.
- Failing to Distribute Required Health Plan Notices
– Employers must provide various health plan notices during open enrollment, such as the Summary of Benefits and Coverage (SBC), COBRA notices, CHIP notices, WHCRA notices, Medicare Part D disclosures, and HIPAA privacy notices. These notices ensure employees are informed of their rights and plan details and must be delivered in timely fashion. Electronic delivery is often permitted with proper safeguards.
- Not Providing Materials to All Eligible Individuals – It’s crucial to distribute open enrollment information not only to active employees but also to eligible individuals on leave, furlough, or COBRA continuation. A multi-channel approach with diligent tracking of distribution reduces the risk of missed communications and potential disputes.
- Neglecting Disclosure of Reasonable Alternatives in Wellness Programs – Wellness programs that impose surcharges or provide rewards based on health standards must offer reasonable alternative ways to meet requirements, per HIPAA rules. Employers need to disclose these alternative standards and provide contact information and assurance that personal physician recommendations will be accommodated. Compliance reduces legal risks related to premium surcharges and discrimination claims.
By proactively addressing these areas, employers can help employees confidently choose benefits while reducing compliance risks and administrative challenges.
by admin | Oct 7, 2025 | Custom Content, Employee Benefits
Health Insurance today is significantly more complex for young workers than it was just a decade ago. This complexity is driven in large part by healthcare costs that have outpaced inflation, pushing premiums, copays, and other out-of-pocket expenses to comprise substantial portions of their budgets. For many younger employees, navigating this landscape is confusing – more than 50% of Gen Z and Millennial workers admit to randomly selecting a health insurance plan, and nearly half say they don’t know where to turn for help during open enrollment. This lack of guidance makes it difficult for them to anticipate costs and make informed decisions about their care.
They also don’t truly grasp basic health insurance terms like “premium” or “deductible.” This knowledge gap doesn’t just confuse employees; it costs businesses an estimated $106 billion to $238 billion annually due to poor health literacy.
The good news? We can turn the tide. Empowering employees to become smarter benefits consumers pays off for everyone, leading to better health outcomes and lower costs. The earlier this education begins, the greater the impact. Here are five practical strategies for helping young employees get up to speed on their benefits:
- Begin with the Basics – Assume nothing. Most employees, particularly those just starting out, aren’t familiar with insurance jargon. Start with “Benefits 101” initiatives that cover the absolute basics: common terms, the ins and outs of group health coverage, vesting schedules, and enrollment period restrictions. Laying this groundwork early helps ensure young employees can make the most of their benefits from day one.
- Highlight the Personal Value – Young employees want to know, “What’s in it for me?” Beyond basic definitions, highlight how a deeper understanding can translate into real-world savings. Explain provider networks and demonstrate how a little research can save thousands on medical procedures.
- Mix Up the Messaging – Traditional handouts are helpful, but young employees often engage more with dynamic content. Use a variety of formats—emails, videos, infographics, flyers, posters, and interactive presentations—to make benefits education more appealing and memorable. A diverse approach ensures the message reaches everyone.
- Make Education Ongoing – Benefits education shouldn’t be a one-time event. Start as soon as employees are hired and keep the conversation going year-round. Regularly discuss relevant topics, such as how to handle life events, use telemedicine, fill prescriptions, or choose between urgent care and the ER. Consider implementing a consistent communication schedule, tackling different benefits topics each month to keep knowledge fresh, especially as open enrollment approaches.
- Offer Personalized Support – Even with great resources, some employees will still have questions. Designate an HR team member as the go-to benefits expert, available for email, virtual, or in-person support. Encourage all employees to meet with HR at least once before open enrollment and consider one-on-one sessions to address individual concerns.
It’s up to employers to help their teams understand and use their benefits wisely—especially young employees who can’t be expected to make informed decisions without a solid grasp of the basics. The real-life reasons people give for delaying or avoiding care—or choosing an ER visit over a primary care doctor—are a powerful testament to why this education is so critical. By investing in benefits education, employers set everyone up for better health, financial security, and peace of mind.

by admin | Sep 30, 2025 | Custom Content, Employee Benefits
 Open enrollment doesn’t have to be a stressful administrative task. When planned well in advance, it becomes a valuable opportunity to review and enhance your benefits offerings, demonstrating your commitment to your team’s physical, mental, and financial well-being. A well-executed open enrollment can boost employee morale, improve retention, and ensure your workforce is supported.
Open enrollment doesn’t have to be a stressful administrative task. When planned well in advance, it becomes a valuable opportunity to review and enhance your benefits offerings, demonstrating your commitment to your team’s physical, mental, and financial well-being. A well-executed open enrollment can boost employee morale, improve retention, and ensure your workforce is supported.
Use this checklist to guide your organization through a successful open enrollment period, from the initial planning stages to the final follow-up.
Phase 1: Plan and Prepare Early (8-12 Weeks Before)
- Leverage technology: Consider a benefits portal where employees can easily access health plan documents such as benefit summaries, plan flyers, and contributions charts.
- Gather Employee Feedback: Solicit and record employee questions, concerns, and suggestions from the previous year. Consider conducting a survey to understand what benefits or improvements your workforce desires for the upcoming year.
- Evaluate and Enhance Offerings: Identify new or updated enrollment options.
- Develop Core Resources: Begin preparing your benefits guide and consider implementing or updating online enrollment tools and software.
- Create Educational Content: Produce digital educational materials like FAQs and videos.
Phase 2: Communication Kick-Off (4 Weeks Before)
- Launch Communication Campaign: Start sharing enrollment information across all selected online platforms (e.g., intranet, company newsletter, email).
- Equip Management: Develop a resource kit for your management team, including talking points and FAQs, to ensure they can confidently discuss open enrollment with their teams.
- Integrate Reminders: Add open enrollment reminders and key dates to the email signatures of your management team.
Phase 3: The Final Countdown (1-2 Weeks Before)
- Host Informational Sessions: Schedule and host virtual benefits meetings, webinars, and one-on-one sessions as needed to answer specific questions.
- Distribute Physical Materials: Provide informational pamphlets and mailers to employees.
- Prepare for Questions: Have answers ready for FAQs to ensure a smooth process.
Phase 4: During Open Enrollment
- Ensure Full Distribution: Make sure every employee receives the following information:
- The open enrollment timeline and deadlines
- A statement of their current coverage
- Information on plan-specific changes and rates
- Summaries of available plans
- The open enrollment booklet and any necessary forms
- Contact details for all plan carriers
- Promote Discussion: Remind managers to actively discuss benefit options with their teams.
- Provide Support: Offer ample time for enrollment and send frequent reminders throughout the period.
- Last-Minute Reminder: Schedule a company-wide reminder for the day before the enrollment deadline to prevent employees from missing the window.
Phase 5: Post-Enrollment Actions (1-2 Weeks After)
- Audit and Submit: Review all enrollment forms for missing or incorrect information.
- Ensure Compliance: Confirm that all relevant health care reform requirements have been met.
- Follow Up: Collect feedback from employees on their open enrollment experience.
Bonus Tip for Success
Consider holding a separate, off-cycle enrollment period to highlight voluntary benefits that might be overlooked during the busy primary open enrollment. This provides employees with a dedicated opportunity to explore additional benefits, potentially increasing your overall benefits utilization and employee satisfaction.
We are here to help; reach out to us with any open enrollment questions or needs you may have!

by admin | Sep 8, 2025 | Custom Content, Employee Benefits, Health Insurance

When navigating the world of health insurance, you will likely encounter the term PPO (Preferred Provider Organization). A PPO plan – whether medical or dental – is about balancing the cost and convenience of care. With a PPO plan, you get the flexibility to see a wide range of doctors. You’ll save money by staying within the plan’s network of preferred providers, but you can still choose to go out of network and receive partial coverage. Unlike some other plans, a PPO allows you to see specialists without a referral.
How a PPO Works
A PPO plan functions much like other health insurance plans, but with a key difference in how it handles providers. The plan pays its contracted providers a set, pre-negotiated rate for services. Because of this arrangement, you pay less in cost-sharing—such as copays or coinsurance—when you receive care from an in-network provider.
While PPO plans offer the flexibility to see out-of-network providers, your costs will be significantly higher. You will likely pay more and may need to submit an insurance claim yourself. It’s also important to note that most PPO plans have a separate out-of-network deductible that you must meet before your plan benefits will begin to cover those costs.
Key Advantages of a PPO Plan
PPO plans are often chosen for their flexibility and convenience. Key benefits include:
- No Referrals Needed: You do not need a referral from a primary care provider to see a specialist. You have the freedom to schedule an appointment with any in-network specialist at any time.’
- Out-of-Network Coverage: You can choose to see providers outside of the plan’s network, which is particularly beneficial for those who travel frequently or live in different states.
- Large Provider Networks: Many PPO plans have a broad, nationwide provider network, offering a wide range of choices for care.
- No PCP Requirement: Unlike some other plan types, you are not required to choose a primary care provider(PCP).
PPO vs. HMO: The Main Differences
The primary difference between a PPO and an HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) plan lies in their approach to networks and referrals.
An HMO plan typically provides coverage only for services received from providers within its network, except in emergency situations. You are also required to choose a primary care provider and obtain a referral to see a specialist. HMO plans often come with lower premiums, but they offer less flexibility.
A PPO plan, on the other hand, gives you greater freedom. You can see specialists without a referral and have coverage for out-of-network care (albeit at a higher cost). While premiums are generally higher for a PPO, the added flexibility can be a major advantage for those who prioritize choice in their healthcare.
Ultimately, choosing the right health and dental plan depends on your individual needs and priorities. By understanding the core principles of a Preferred Provider Organization, you can make a more informed decision that aligns with your lifestyle and ensure you get the most value from your benefits.

by admin | Sep 2, 2025 | ACA, Compliance, Employee Benefits
 How to position yourself as a trusted ACA compliance advisor
How to position yourself as a trusted ACA compliance advisor
For brokers and benefits advisors, Q4 planning doesn’t start in October. It starts now.
September marks a critical moment in the annual ACA compliance cycle, when employers begin thinking about year-end strategies, benefits renewals, and how to avoid last-minute reporting panic. That makes now the perfect time to deepen your role as a strategic advisor and help clients get ahead of the curve.
Here’s how you can stand out by guiding clients through ACA compliance before it becomes a scramble, and why it will pay dividends well into 2026.
📌 Step 1: Help Clients Take Stock of Their Workforce Now
The foundation of ACA compliance is accurate employee classification. Yet many employers still struggle to determine:
Brokers can add immediate value by helping clients audit their headcounts and hours before Q4 begins. That insight informs both ACA reporting and benefits planning decisions, and helps prevent costly missteps when deadlines hit.
🧠 Step 2: Educate on What’s Changed and What’s Coming
ACA rules don’t change often, but confusion persists. Many clients are unaware of:
- State-specific ACA mandates (California, New Jersey, Rhode Island, Vermont, Massachusetts, and Washington DC)
- Updated penalty thresholds and IRS enforcement priorities
- New reporting formats or system changes that could impact submissions
Providing timely updates and checklists positions you not just as a broker but as a compliance partner. You can even use these touchpoints to introduce solutions like ACA reporting automation or integrated compliance tools.
📊 Step 3: Map Out a Reporting Game Plan Before the Crunch
ACA compliance starts with good planning, and now is the time to get ahead. By August, many employers are wrapping up plan design decisions for the next year, making it an ideal time for brokers to:
- Review last year’s filing process (what worked and what didn’t)
- Flag missing or incomplete employee data
- Identify vendors or tools that can simplify electronic filing
- Offer ACA services or connect clients to trusted platforms
The earlier your clients begin organizing data and confirming eligibility, the fewer errors and penalties they’ll face later. And the more indispensable you become in their eyes.
🎯 Position Yourself as the Solution, Not Just the Messenger
ACA compliance is often seen as a burden. But for brokers, it’s a huge opportunity to differentiate. Instead of only alerting clients to upcoming requirements, step in as the solution:
✅ Offer ACA strategy sessions during annual benefits reviews
✅ Share tools and resources that support self-filing or full-service options
✅ Leverage partnerships with platforms like Mitratech Mineral to deliver expert-backed compliance
When you help clients manage risk and reduce workload, you go from being a benefits provider to a business advisor and partner.
🗓 Ready to Dive Deeper?
Join us for a special webinar:
Beyond the Basics: Mastering ACA Compliance for Multi-State Employers
📅 Thursday, September 18, 2025 | 1:00 PM ET
🎙️ Featuring Angela Surra, Principal Benefits Expert at Mitratech Mineral
👉 Register Now
Final Thought
The best brokers know that compliance isn’t a once-a-year conversation, it’s an ongoing strategy. By helping your clients get ACA-ready now, you’re not just solving a problem. You’re showing up as the expert they trust to protect their business, simplify their operations, and keep them ahead of what’s next.
Looking for the right tool to help your clients stay compliant and stress-free? The ACA Reporting Hub from Mitratech Mineral is purpose-built to support brokers and the employers they serve. Whether you’re offering ACA as a service or guiding clients through self-filing, our platform combines automation with compliance expertise to simplify the entire process.
By Brian Costello
Originally posted on Mineral.com

 No doubt about it, prescriptions are expensive. While this may not be a big worry when you’re young and healthy, the costs can add up quickly if you’re diagnosed with a chronic condition or need an expensive drug. Whether you take medications regularly or for an occasional illness, it pays to know how to save money on prescriptions.
No doubt about it, prescriptions are expensive. While this may not be a big worry when you’re young and healthy, the costs can add up quickly if you’re diagnosed with a chronic condition or need an expensive drug. Whether you take medications regularly or for an occasional illness, it pays to know how to save money on prescriptions.





