
by admin | Jul 28, 2020 | COVID-19, Human Resources, Work From Home

“When people are financially invested, they want a return. When people are emotionally invested, they want to contribute.” – Simon Sinek
The COVID-19 pandemic has taught us many things. First, it has taught us that empathy and kindness goes a long way. We’ve learned that as individuals, communities, and as a nation, that we can do hard things when we work together. Finally, this pandemic has taught us that the relationship between employer and employee is a valuable one. How much the employee feels valued by their employer is called “engagement.” And this feeling of value is one that more and more companies are investing in in a post-COVID environment.
Employee engagement is when an employee feels “high levels of involvement (passion and absorption) in the work and the organization (pride and identity) as well as affective energy (enthusiasm and alertness) and a sense of self-presence.” Let’s dive in and look at some fast facts on this subject and how to increase engagement in this new workspace we have found our world occupying.
BY THE NUMBERS
- 34% of employees and 35% of employers stated they felt engaged in their work in a 2019 Gallup poll.
- 38% of employees now say they are “highly involved in, enthusiastic about and committed to their work and workplace” via a May 2020 Gallup poll.
- This is the highest reported engagement since Gallup began measuring this topic in 2000.
BOTTOM LINE
- Unengaged employees lower productivity, innovation, and the bottom line.
- Engaged employees have lower absenteeism and lower turnover.
- When an employee believes that they are being heard and seen as a valued investment, they feel empowered to do their best work.
- Teams that report being engaged in the workplace have 21% higher profitability than those who report being unengaged.
HOMESCHOOL
- One way to create engagement in the workplace is to promote learning opportunities at home for employees. This can be done in virtual workshops for remote workers.
- If a company’s investment is in learning and development, this shows the employee that their employer sees their future as important.
- Positive results of investing in workforce education include increased employee engagement, more innovation, and increased understanding of the company’s goals.
- Remote employees who participate in a company’s virtual training report that beyond the educational benefit they receive, they also feel as though they are being equipped with new skills for handling stressful situations once they are able to return to work.
RESOURCES
There are numerous blogs and articles and creative educational interaction sites to keep employees engaged and learning while remote. Below are some fun and creative sites to help you create your own engagement campaign for your organization.

by admin | Jul 21, 2020 | Human Resources, Workplace
 The hardest thing about the future of work is defining the concept. The chief reason has to do with change. It’s constant with new technologies coming online at an increasing pace and changing the way people complete their work.
The hardest thing about the future of work is defining the concept. The chief reason has to do with change. It’s constant with new technologies coming online at an increasing pace and changing the way people complete their work.
If the data is to be believed, what HR knows about work is quickly disappearing. Korn Ferry predicts by 2030 a global human talent shortage of more than 85 million people will exist. That’s an astonishing prediction, but changes are expected well in advance of that year. Forty percent of today’s Fortune 500 companies, according to Deloitte, won’t exist in 2025. Additionally, the World Economic Forum predicts 133 million new jobs will be developed by 2022 through artificial intelligence.
For HR, this data points to a very clear path: prepare your company now for the work of the future.
“The fact is we can guess all we want, but we can’t ever truly know what the future holds,” excites Granite Group chief people officer Tracie Sponenberg.”
Despite all the difficulty in defining the future of work and some of the concerns that come with it, Sponenberg said there is some excitement to be had. Other HR professionals agree.
“What excites me most are the new technologies that are going to support employees in making leaps in speed, agility, efficiency, productivity and overall performance,” Andrew Saidy said.
He’s the vice president of talent digitization, employer branding and university relations for Schneider Electric. As the digital transformation of HR continues, we’ve certainly seen advancements in those specific areas. Employees are using more tools that are either digital in part or completely so. Both help employees increase efficiency which leads to an increase in productivity and performance. Technology has also allowed companies to be agile in their approach to work.
GE Healthcare head of global digital learning Christopher Lind agrees with Saidy saying technology helps organizations break all the rules when it comes to connecting, collaborating and experiencing work. Even so, he acknowledges there is still some fear around technology.
“Instead of being afraid of machines taking our jobs, I believe we should be excited that machines can do the rudimentary things we waste so much time doing, so we can focus on the higher order things that really drive us,” Lind said.
Learning and Development
Despite Lind’s statement, there is still some concern around the potential loss of jobs to technology solutions — specifically around artificial intelligence and automation.
It might surprise you to know that’s not an uncommon feeling to have. There have been concerns about technology taking away jobs since the First Industrial Revolution in the early 1900s. Here we are 100 or more years later entering the Fourth Industrial Revolution and we’re experiencing similar concerns. While that’s an understood feeling, HR needs to help move the workforce away from this type of concern and focus more on skilling accordingly… what is, sometimes, referred to as future-proofing skills. That’s really the name of the game.
During this particular revolution, new industries and roles will be created. Forrester predicts robots, AI, machine learning and automation will create 9 percent of new jobs by 2025. Some of the new jobs expected to be created include:
- Robot monitoring professionals
- Content curators
- Data scientists
- Automation specialists
Naturally, some will go away. By 2025, Forrester also predicts those same technologies will replace 16 percent of US jobs. Most of the impact will be felt on office and administrative support staff roles as well as roles where workers have a low amount of formal education – the so-called “at-risk jobs”. Learning new skills and building on existing competencies will be crucial to companies wanting to remain competitive in the current climate. The challenge there lies in trying to figure out which skills your employee will need.
The data provided gives HR some indication on where to begin. With more robot, artificial intelligence, automation, and other related jobs expected in the future, employees should start building their knowledge and skill base now.
While it seems daunting, there is some good news. A World Economic Forum and Boston Consulting Group report says “95 percent of at-risk U.S. workers could be successfully retrained for jobs that pay the same as or more than their current positions and offer better growth prospects.”
So How Does HR Move Forward?
Taking employees off-line for weeks to train is pretty much a “no go” at this point in the game. Learning and training almost have to be conducted “on the job” in reality. This isn’t just a need. Many employees actually prefer learning on the job. Keeping up workflow and productivity is important to the continued success of the business. Different companies are using different methods to accommodate this need.
Walmart, for instance, has automated tasks at their stores such as customer checkout. That means associates have more time to train on a multitude of concepts including customer service.
The department store giant is using virtual reality to simulate different issues their associates will experience during their employment. For instance, VR is being used to simulate Black Friday rushes.
AT&T is taking a different approach. The company has instituted a program called “Future Ready”. Essentially, the $1 billion, web-based initiative includes online courses through a myriad of vendors and universities. This allows employees to figure out what skills they need and train for the jobs the company needs right now and will need in the future. Their online portal, called Career Intelligence, allows workers to see available jobs, the skills each requires, the suggested salary and whether or not the area is expected to grow or shrink in the future. It is career pathing at its best and allows employees to figure out how to get from where they are now to where they want to be and the company needs them to be in the future.
By Mason Stevenson
Originally posted on hrexchangenetwork.com
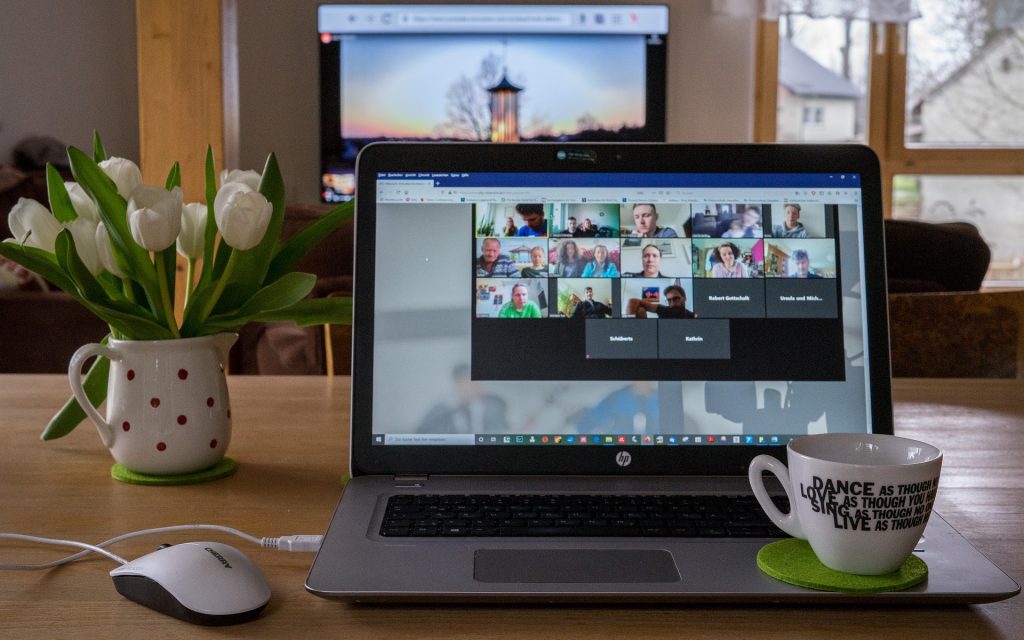
by admin | Jul 15, 2020 | Human Resources, Work From Home
 Even with video conferencing and messaging apps, fully involving remote employees in team and company meetings remains a challenge. There may be no replacing the experience of being physically in the room, but you can take steps to make meetings more productive and inclusive for remote participants.
Even with video conferencing and messaging apps, fully involving remote employees in team and company meetings remains a challenge. There may be no replacing the experience of being physically in the room, but you can take steps to make meetings more productive and inclusive for remote participants.
The most important thing to remember when “meeting” with remote employees is that you can’t conduct the meeting in the same way as you normally do when everyone is physically present. You have to find a way to replace the advantages that close proximity has, especially the ease of reading body language and picking up social cues. These, unfortunately, do not translate well over the screen or the phone. So, what can you do?
What remote employees need to fully participate in meetings is space and time to speak. You can provide this space and time in a few ways.
First, ask any physically present participants to pause for a second before jumping into the conversation. This gives remote employees time to get a word in, plus it helps counter any time delays caused by the conferencing technology. Second, whoever is leading the meeting should regularly invite remote employees to add anything if they have something to say, preferably before moving on in the agenda. Third, when possible, have one or more remote employee lead the meeting or a section on the agenda. This focuses attention on the remote speakers and can help remind everyone that the meeting isn’t just happening in one physical room. Finally, if your remote employees are located in the same workspace, occasionally setting their site as the physical meeting space can help your non-remote employees get a feel for the challenges of being remote during a meeting.
Some preliminary work before the meeting can also help make the meeting itself more efficient. First, test any systems ahead of time so that they’re working for everyone when the meeting starts. Second, email the agenda out so everyone knows what to expect. Third, assign someone in the meeting room to be the contact person that remote employees can email or message if they have questions, concerns, or issues.
After the meeting, check in with any remote employees and ask them to be candid about their experience. What worked well and what could be improved? See what you can do to accommodate them in the next meeting.
You may not be able to fully replicate the experience of physically being in the room, but taking these steps can enable remote employees to feel more involved and make the meeting itself run more smoothly.
By Kyle Cupp
Originally posted on thinkhr.com

by admin | Jul 9, 2020 | Hot Topics
 “Everyone learns differently” is a phrase we have all heard at some time in our educational endeavors. It may have been overheard from your parents as they explained to your teacher why you have to get up and move all the time during class. You may have heard it said in high school as a communications teacher gave you examples of learning styles. This phrase may have even been said recently as you sat through a leadership seminar at work as the presenter encouraged you to speak to the different learners you will encounter at the office. Whatever the case, it’s true! Now, let’s learn!
“Everyone learns differently” is a phrase we have all heard at some time in our educational endeavors. It may have been overheard from your parents as they explained to your teacher why you have to get up and move all the time during class. You may have heard it said in high school as a communications teacher gave you examples of learning styles. This phrase may have even been said recently as you sat through a leadership seminar at work as the presenter encouraged you to speak to the different learners you will encounter at the office. Whatever the case, it’s true! Now, let’s learn!
Three Types of Learners
- Visual—This is the biggest population of learners out there. A whopping 65% of people say they best learn with visual aids. These learners will be the ones doodling during your meeting or taking copious notes. They are the group that says, “Don’t read it to me. I need to see it.” Your creative types in the office will most likely fall into this category.
- Auditory—Our next learning group (30%) is made up of those learners that need to hear it out loud to retain information. As you interact with and lead your auditory learners, remember that your voice is important to their understanding of the subject matter. Fluctuate your tone and pitch. Ask open-ended questions so that they can verbalize delivered information. And, most importantly, this group learns best in discussions and oral presentation.
- Kinesthetic—Move it or lose it (their attention). Kinesthetic learners make up only 5% of the population but they are probably the group you notice the most. Why? Because they will be the ones that cannot sit still during a meeting or training. They thrive on movement so give them a team challenge to reinforce your training subject matter. Make sure you are also giving this group lots of breaks in your training time.
How to Make This Work Remotely
The workforce has displayed a great ability to work remotely with a reported 17% of companies moving to work-from-home organizations. This work-from-home model does have a drawback, though, in that it is more difficult to train employees with different learning styles. But this doesn’t have to be the case!
Helpful Tips to Training Three Types of Learners
- When you are creating materials for trainings, make sure you create things that appeal to all three learners but don’t lean too hard on one style.
- Your resources should be easily accessible from a home office (email) and content easily digestible. Remember, though, that not all learners can retain information in written form so make sure there’s an option for visual and kinesthetic styles.
- Recreate the sociability of the in-person office for the remote office. Encourage online meeting websites for teams such as Zoom and Skype. This allows your employees the chance to see their coworkers face to face and retains comradery.
- Offer continuing education through online training sites such as lessonly.com. This site appeals to the three learning styles by training through video (visual learner), spoken word (auditory learner), and movement (kinesthetic learner: typing, moving mouse, etc.).
With three types of learners, it is often overwhelming for trainers as they prepare for and deliver their educational sessions. However, it is not impossible! By identifying the type of learner you’ll interact with, you can prepare supportive materials that best speak to each group. Visual, Auditory, and Kinesthetic learners have one thing in common—they are eager to work and contribute to their company.





